Starting a new project, whether designing a product or improving a process, always comes down to one critical factor: cost. Project cost management is about understanding how expenses, from resources to team salaries, impact the company‘s bottom line. With limited funds, setting and sticking to a budget is essential to ensure the project‘s success doesn‘t jeopardize the company‘s financial stability.
What is cost management in project management?
Cost management in project management is all about keeping your project‘s finances under control. Think of it as the process that ensures you‘re spending your money wisely throughout the life of the project. From planning how much you‘ll need to spend, to keeping an eye on actual costs, and making sure everything stays within the budget, cost management is crucial for the success of any project.

Cost management in project management involves:
- Cost estimation
Estimate all expected expenses, including labor, materials, and equipment. This gives you a starting point for your project‘s budget.
- Budgeting
Create a budget based on your estimates. This budget sets spending limits for different parts of the project, helping you manage finances effectively.
- Cost control
Monitor spending throughout the project. Compare actual costs to your budget and make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
- Cost reporting
Regularly update your team and stakeholders on the project‘s financial status. This helps catch any issues early and keeps everyone informed.
- Cost forecasting
Predict future costs based on current trends. This helps you anticipate and manage potential budget challenges before they arise.
Good cost management is like having a safety net for your project. It helps you avoid surprises and ensures you have enough resources to complete the project successfully. Without it, you risk running out of money, which could delay the project or force you to cut corners. In short, cost management keeps your project financially healthy and on track.
Types of project costs in project cost management
Planning the project budget is a big part of project cost management that seems like a daunting experience. As a rule of thumb, here are some main elements to include in project cost estimates.
- Pre-project Planning
These costs can vary significantly in each industry and is reliant on the use of outside consultants. However, this cost generally includes conducting market research, securing materials, setting up the workspace, and selecting managers and employees. - Materials
Every material related to the completion of the project falls in this category. For example, if the company is rolling out a new publication, the printing costs, including ink and paper, would have to be accounted for in the budget. - Personnel Costs
Projects are not completed without human resources. This could include everyone from the project manager to the cleaning people. Benefits and insurance are also a consideration of these costs. Any contributions by part-time staff are also considered in personnel costs. - Operating and Non-Operating Expenses
Any fees associated with the project, such as permitting costs, inspections, delivery of supplies, marketing, advertising, and technology costs, are classified as operating expenses.
Non-operating expenses include costs that don’t involve customary activities or are related to production. These would consist of relocation costs, interest payments, and other costs from financial obligations and not related to the business’s primary operations.
The above costs are also grouped into labor and non-labor costs.
Labor costs comprise the effort hours of each personnel resource multiplied by their hourly cost. Consulting or contract services are external labor costs that are estimated with their hourly rate. If this cannot be precisely accounted for, estimates can be used based on a standard cost range. This personnel can include accountants, programmers, and administrators.
Internal labor costs may already be accounted for in the department‘s budget, so additional costs would be zero. However, any further costs above what is included would be budgeted as well.
Non-labor costs include everything outside the above-described salary and outside contractor costs. These can consist of hardware, software, equipment, travel expenses, and supplies.
Key project cost management metrics
Now that the project is well underway, how do you determine everything is staying within budget? Several metrics are used in project cost management to ensure how the project is coming along cost-wise.
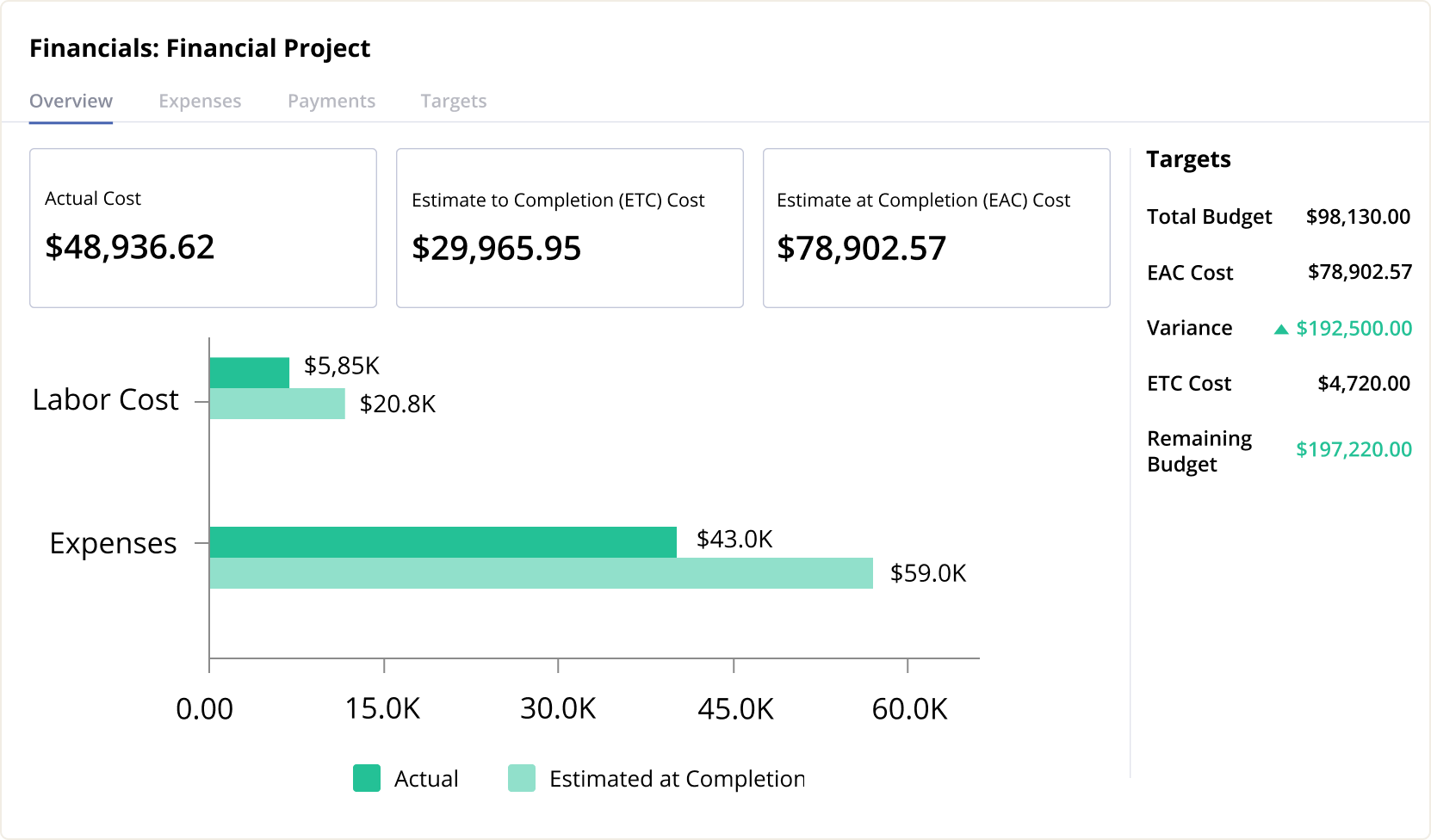
- Estimate to Complete (ETC)
The ETC is a measurement of the forecast of the costs remaining for project completion. This figure is calculated by adding estimated labor and non-labor costs required to complete the project. - Estimate at Completion (EAC)
The EAC metric is calculated by combining the present cost with ETC Cost. Comparing EAC with other metrics can determine if the project is running within budget and on time. Since project statuses can experience fluctuations over time, managing EAC is an essential process. - Cost Variance
This metric measures the budgeted amount minus the money spent. If the value is positive, then the project is within budget. However, a negative result means that you’ve spent more than was initially allocated. This metric is used to assess overall progress. It goes without saying that if you have used up 30% of your budget in the first two months of a one-year project, there may be an issue.
Project cost management plan: how to calculate project costs
Accurate project cost management, including calculating project costs, is essential for staying within budget and ensuring project success. Follow these steps to estimate your project costs effectively:
1. Define the project scope
Clearly outline all tasks, deliverables, and activities involved in the project. Understanding the full scope ensures all potential costs are considered.
2. Break down the project into tasks
Divide the project into smaller, manageable tasks. Identify the resources needed for each task to assign specific costs.
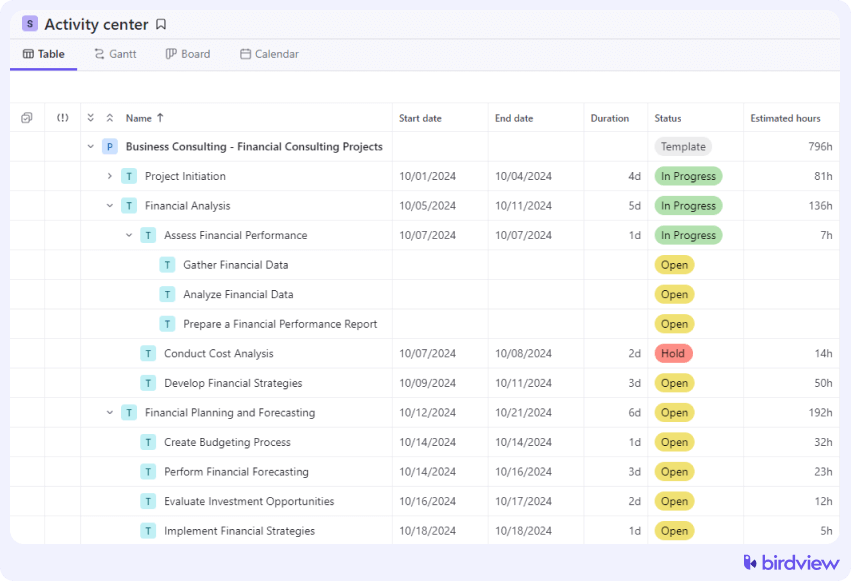 3. Estimate direct costs
3. Estimate direct costs
Direct costs are expenses tied directly to the project.
- Labor costs: Multiply each team member‘s hourly rate by the hours they will work on the project. Include full-time, part-time, and contractor costs.
- Material costs: Estimate the cost of all physical materials required, such as raw materials and supplies.
- Equipment costs: Include costs for purchasing, leasing, or maintaining any necessary equipment.
4. Estimate indirect costs
Indirect costs are necessary but not tied to specific tasks.
- Overhead costs: Include general business expenses like utilities and rent.
- Project management costs: Account for costs like software licenses and communication tools.
- Training costs: Include any costs for training or development required for the project.
5. Include a contingency reserve
Set aside a contingency reserve (typically 5-10% of the total budget) to cover unexpected costs and prevent budget overruns.
6. Calculate total project costs
Add up all direct and indirect costs, plus the contingency reserve, to determine the total project cost:
Total project cost = direct costs + indirect costs + contingency reserve
7. Use project management software
Use software like Birdview PSA for project cost management to automate cost estimation, track expenses in real time, and adjust forecasts as needed. This ensures accurate and up-to-date project financials.
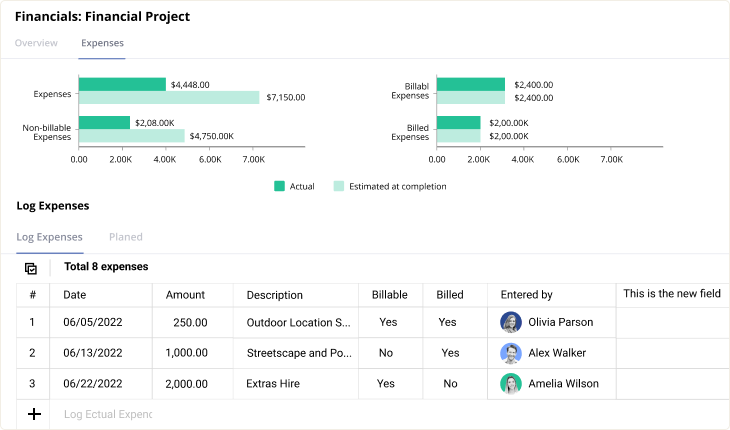
Example: For a construction project with $200,000 in labor costs, $300,000 in materials, $50,000 in equipment, and $100,000 in indirect costs, adding a 10% contingency reserve would bring the total project cost to $715,000. Birdview can help you monitor these costs to stay on budget.
What are the benefits of project cost management
- Budget adherence
One of the primary benefits of cost management is ensuring that the project stays within its budget. By closely monitoring expenses and tracking them against the budget, you can avoid overspending and make adjustments as needed to keep the project financially on track.
- Improved resource allocation
Cost management allows you to allocate resources more efficiently. By understanding the costs associated with each task and resource, you can ensure that resources are used where they are most needed and that unnecessary expenditures are minimized.
- Enhanced decision-making
With accurate cost data at your disposal, you can make more informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle. Whether it‘s reallocating budget, adjusting project scope, or addressing unexpected costs, having a clear understanding of your financial standing enables better decision-making.
- Increased profitability
For billable projects, effective cost management directly impacts profitability. By keeping costs under control, you maximize the profit margins on the project, ensuring that the revenue generated leads to tangible gains for the business.
- Risk mitigation
Proactive cost management helps identify potential financial risks early on. By tracking expenses and comparing them to the budget, you can spot warning signs such as cost overruns or resource shortages, allowing you to take corrective action before they become bigger issues.
- Stakeholder confidence
Effective cost management builds trust with stakeholders by demonstrating that the project is being managed responsibly. Regular financial reports and transparency around costs reassure stakeholders that their investment is being handled wisely.
- Improved project outcomes
Ultimately, good cost management contributes to better project outcomes. By managing costs effectively, you ensure that the project can be completed on time, within scope, and with the desired quality, leading to greater overall success.
What are the challenges of project cost management
While cost management is essential for project success, it comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges can help you better prepare and address them as they arise:
1. Accurate cost estimation
One of the biggest challenges in cost management is accurately estimating the costs at the beginning of the project. If initial estimates are too low, the project may face budget shortfalls, leading to delays or compromised quality. Conversely, overestimating costs can result in inefficient use of resources and higher-than-necessary budgets.
2. Scope changes
Projects often undergo scope changes due to evolving client requirements, unforeseen issues, or new opportunities. These changes can lead to additional costs that were not originally planned for, making it difficult to stick to the initial budget.
3. Unforeseen expenses
No matter how well you plan, unexpected costs can arise, such as sudden price increases for materials, unexpected regulatory requirements, or equipment failures. Managing these unforeseen expenses without derailing the project can be challenging.
4. Resource allocation
Balancing the allocation of resources is another challenge. If resources are not allocated efficiently, you may end up with overstaffed tasks draining the budget, or understaffed tasks causing delays and additional costs to catch up.
5. Maintaining cost control
Even with a budget in place, maintaining strict cost control throughout the project can be difficult. This requires constant monitoring, regular reporting, and timely intervention when costs start to deviate from the plan. It‘s easy for costs to spiral out of control if vigilance is not maintained.
6. Communication with stakeholders
Keeping stakeholders informed about cost management can be challenging, especially when there are budget overruns or financial issues. Transparent and regular communication is necessary to maintain stakeholder trust, but it can be difficult to convey complex financial information in a way that is easily understood.
7. Integrating cost management with other project processes
Cost management doesn‘t operate in isolation; it needs to be integrated with other project management processes like scheduling, resource management, and risk management. Ensuring that all these elements work together seamlessly can be a complex and challenging task.
8. Technology limitations
While project management software can greatly assist with cost management, it‘s important to choose a tool that meets the specific needs of your project. If the software lacks necessary features or is difficult to use, it can hinder rather than help your cost management efforts.
How to calculate project profitability
In the case of billable projects, every manager hopes their project turns a profit for the company. The profitability of the work can be determined by calculating the net profit and net profit margin.
Project profit is measured with the following formula:
Project Profit = Project Revenue – Project Costs
The net profit margin is the ratio of net profits to revenues. This result is a percentage that shows how much of the revenue translates to profit. The formula for net profit margins is as follows:
Net Profit Margin = Total Revenue – Total Costs/Revenue x 100
The net profit margin reveals the accurate profit generated after accounting for all expenses. This metric can be tracked over time to help forecast profits.
Example: Imagine a scenario where a software development firm undertakes a client project with a budget of $500,000. Throughout the project, Birdview‘s software tracks all costs related to development, testing, and deployment. If the project‘s total cost is $450,000 and the revenue generated is $550,000, Birdview will calculate a net profit of $100,000 and a net profit margin of 18.18%. This allows the firm to understand the profitability of the project at a glance and make informed decisions for future projects.
What is project billing (revenue)?
Project cost management best practices
Project cost management during the course of the project is a crucial responsibility of management. The following are some best practices for managing project costs.
- Establish Clear Cost Controls During Planning
Controlling project costs means establishing controls for each expenditure. Even though unexpected expenses may arise, proper preparation for them ahead of time can reduce risks. Making a to-do list of costs should be considered as a first step. This should include fixed costs, such as permits and taxes, as well as other industry-related fees. Plan on who will oversee, approve, and sign off on expense elements. - Plan Labor Costs
Personnel costs, including salaries and overtime, are essential aspects to consider when planning and managing project costs. How many employees are needed, their roles, and pay ranges should be included in labor cost estimates. When planning your project, simply assign the relevant Rate Card to each team member, and Birdview will automatically calculate the total labor costs based on the hours assigned to each role.

- Track Cost Metrics Regularly
Calculating metrics at the end of each reporting period can ensure the project stays within budget. Doing this regularly can keep expenses down since action can be taken sooner to control unexpected costs.
- Continually Track Project Scope
New client requirements and other changes can quickly arise, which can mean added costs and more work. Regularly tracking the scope will avoid losing track of these issues. - Use Cost Forecasting Tools
Accurate forecasting is key to preventing budget overruns. Update cost forecasts based on current project data regularly to adjust resources and timelines as needed to stay on track. Birdview‘s forecasting tools allow for dynamic updates to your project‘s budget, giving you a clear view of projected costs and any potential financial risks. - Monitor Project Health
One of the most effective project cost management methods is constant project monitoring. For instance, Birdview uses trouble indicators that provide real-time alerts when any aspect of your project deviates from its planned parameters, such as budget overruns, project deadlines, or overloading. These indicators are made to get your immediate attention and prevent further complications.
Time and Cost Tracking
Automating project cost management tasks
Tracking project costs and expenses is often traditionally done in spreadsheet programs such as Excel. However, this approach has proved to be very tedious and time-consuming, especially if multiple projects are being tracked. Thanks to advances in project management software, this task is accomplished more efficiently.
Today’s Project Budget Management Software tools help manage budgeting, forecasting, and other tasks that can help managers keep on top of all project elements. This software can also assist managers in collaboration and communication with project stakeholders.
At Birdview PSA, our solutions can assist with cost management by setting and tracking budgets and continually monitoring expenses. Our powerful software can accurately monitor project parameters, budgets, and schedule statuses, in addition to producing comprehensive reports for executives and team members. Birdview also integrates seamlessly with other business systems, allowing for a holistic view of project finances and overall business health.
Furthermore, if your company needs to manage a portfolio of projects, you can generate detailed financial reports that aggregate data across all projects, helping you identify trends, allocate resources more effectively, and make strategic decisions to maximize profitability.
Contact us today to schedule a guided tour and see how Birdview PSA can efficiently manage your cost management tasks.


