Project Monitoring and Control is a crucial phase in project management that involves tracking the project’s progress, comparing it against the plan, and making adjustments as necessary. It’s about keeping the project on track and meeting its objectives, deadlines, and budget.
Monitoring and control allow project managers to analyze in real-time whether tasks are being completed on schedule and within budget and make decisions.
Despite its critical role, project monitoring is fraught with pitfalls that can derail even the most meticulously planned projects. Recognizing these common errors is the first step towards avoiding them.
As a careful project manager, you should always “Trust, but check.” Project Monitoring and Control acts like a watchful guard in project management, making sure that every tiny detail gets noticed.
What is project monitoring and control?
At its core, Project Monitoring and Control is about proactive oversight. It’s not merely about checking off boxes or following routines; it’s about peering into the heart of your project with a keen eye, ready to catch the slightest hint of deviation.
Project control includes many steps to carefully monitor the project’s timeline, resources, and expenses. While there are tools to help with project monitoring, understanding the process behind it is crucial, and we’ll delve into this.
The Dual Pillars: Monitoring and Control
Project Monitoring. View monitoring as the heartbeat of your project. It involves constantly gathering information, evaluating progress, and comparing results to initial plans. Think of monitoring as your alert system, giving you a heads-up on problems before they grow bigger.
Project Control. Control is the action arm of this phase. It’s where decisions and actions are taken in response to the insights gained from monitoring. Control ensures that your project remains on course, whether realigning tasks, reallocating resources, or revising strategies.
Birdview empowers managers to make informed decisions quickly. For example, if a project starts to deviate from its planned timeline, Birdview‘s resource management tools allow managers to reallocate resources efficiently to bring the project back on track without compromising other project areas.
The essential role of project monitoring and control
Project Monitoring and Control is more than just a step in the project management process. The core goal is to maintain the project’s health and success. This section explores the necessity of this phase and highlights its influence on different areas of project management.
- Keeping Projects on Target
Project Monitoring and Control’s primary importance is ensuring the project stays true to its original goals. Projects can change over time and might start to move away from their initial objectives. By keeping a close watch regularly, any shifts can be spotted early on, making it possible to take quick actions to correct them. ICS and SCADA systems help with this by providing continuous monitoring and control of industrial operations, giving project managers the real-time data needed to make timely adjustments and keep the project on track. - Risk Management
Every project faces its set of uncertainties and potential risks. Active monitoring provides a proactive stance in identifying risks before they become issues, enabling the project team to implement mitigation strategies effectively and minimize negative impacts on the project. - Resource Optimization
Resources, be they people, budget, or materials, are limited. Project Monitoring and Control ensure these resources are used wisely, avoiding excess and shortfall. It aids in distributing tasks evenly, managing expenses effectively, and providing resources for productive tasks. - Clients’ and Stakeholders’ Satisfaction
Stakeholders, from clients to team members, have vested interests in the project. Through consistent monitoring and control, stakeholders are informed about the project’s progress, changes, and challenges. This transparency builds trust, fosters collaboration, and enhances stakeholder satisfaction. - Schedule and Budget Adherence
One of the most visible signs of a project’s success is its ability to meet the agreed-upon schedule and budget. Through diligent monitoring, potential schedule slippages or budget overruns can be identified and addressed promptly.
Birdview enhances this role by providing advanced analytics and BI reporting tools that offer insights into every project aspect. With these tools, project managers can drill down into specific areas like resource utilization or budget adherence, ensuring that all elements of the project are optimized for success. They also can generate detailed reports that keep stakeholders in the loop with real-time data and build trust between them and your team.
The project monitoring and control process
The project monitoring and control process establishes the foundation of successful project management. This procedure monitors the project’s advancement and challenges, guaranteeing prompt action to maintain the timeline and budget. It allows the project manager to spot problems either in real-time or proactively.
Setting baselines and benchmarks
The process begins with establishing clear scope, time, and cost baselines. These baselines serve as the standard against which all project performance is measured. They are not just reference points but the foundation for effective monitoring.
Ongoing performance tracking
Constantly measuring the project’s performance lies at the heart of monitoring and control. This includes monitoring progress compared to set standards and using different measures and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to check the project’s condition as it unfolds.
Identifying deviations
With data in hand, the process delves into variance analysis, a critical examination of where actual performance deviates from planned performance.
Implementing corrective actions
Identifying variances is only half the battle; the essence of control lies in taking decisive corrective actions. This may involve reassigning resources, adjusting schedules, or revising strategies to bring the project back in alignment with its baselines.
Communication: informing stakeholders and clients
Successful monitoring and control rely on clear and ongoing communication with stakeholders. This keeps everyone updated on the project’s progress, any challenges, and the actions being implemented to resolve them.
Project monitoring and control plan: a step-by-step guide
A robust Project Monitoring and Control Plan is like your project’s guide, helping you keep things moving in the right direction even when things get tough.
Step 1: Establish What You Need to Track.
Start by identifying the elements of the project you need to monitor, such as the scope, timelines, expenses, and any other critical areas pertinent to your project. Setting these objectives lays the groundwork for your overall strategy for monitoring and control.
Step 2: Establish Performance Metrics
Choose specific, measurable indicators that will give you insights into your project’s health. These could range from task completion rates and budget variances to quality metrics and stakeholder satisfaction levels.
Step 3: Set Baseline Measurements
Establish a baseline or target for each metric against which actual performance can be compared. These baselines are your project’s benchmarks and are crucial for identifying deviations requiring corrective actions.
Step 4: Determine Monitoring Frequency
Decide how often you’ll monitor each aspect of your project. While some components may require daily scrutiny, others might need weekly or monthly check-ins. Your monitoring frequency should balance thorough oversight with efficiency, avoiding the pitfalls of micromanagement.
Step 5: Assign Monitoring Responsibilities
Assign team members or stakeholders to monitor specific project components. Ensure each person understands their responsibilities and the metrics they’re expected to track
Step 6: Plan for Variance Responses
Anticipate potential variances and plan how to address them. This involves outlining corrective actions for possible deviations from the baseline measurements and establishing thresholds for when these actions should be triggered.
Step 7: Review and Revise the Plan
Acknowledge that your Monitoring and Control Plan is not set in stone. Schedule regular plan reviews to incorporate lessons learned and adapt to the evolving project landscape.
Step 8: Implement Quality Control Measures
Incorporate quality checks and reviews at critical points in the project to ensure deliverables meet the established standards. Depending on the nature of your project, this could involve peer reviews and client feedback.
Step 9: Review and Revise the Plan
Acknowledge that your Monitoring and Control Plan is not set in stone. Schedule regular plan reviews to incorporate lessons learned and adapt to the evolving project landscape.
Putting project monitoring and control into practice
Project managers often rely on several key performance indicators (KPIs) to track a project’s progress. These KPIs are crucial in assessing the project’s progress towards its goals. Furthermore, project managers use various methods and instruments to monitor and control project aspects.
Establishing a Monitoring Framework
Begin by crafting a framework that outlines what will be monitored, how, and by whom. This framework is your script, guiding the entire monitoring process. Define clear metrics and KPIs that resonate with your project’s objectives.
Assigning Monitoring Roles
Each person in your project has a specific role. It’s important to allocate these tasks thoughtfully, making sure everyone is clear about their responsibilities, from keeping an eye on how things are moving to spot any changes from the plan.
Conducting regular Stakeholder, project team, and client communication
Regular check-ins and review meetings are super important. They help you see how things are going, spot mistakes, and improve. Having these meetings often and keeping them on point is critical.
Using project management software to monitor your project.
Using project management software lets you monitor your project closely as it unfolds. It’s like having a dashboard where you can see everything in real-time, from what tasks are being worked on to how resources are being used.
The arsenal of project monitoring and control techniques
In complicated projects, the project manager usually handles the tracking and guiding of the project. Like leading a big show, you must ensure everything is done right, and nothing is overlooked. Even tasks that seem simple can have unexpected issues.
Earned Value Management (EVM)
EVM is like the spotlight on your project’s financial health, illuminating the actual value of the work completed. It intertwines scope, schedule, and cost, providing a comprehensive view of project performance. By tracking these variables, you’re not just observing; you’re predicting, allowing you to make proactive decisions.
Critical Path Analysis (CPA)
Critical Path Analysis (CPA) helps you see your project as a series of linked tasks. It shows you the most essential path affecting the project’s length. By knowing this critical path, you can determine which tasks are strict on time and which have some wiggle room.
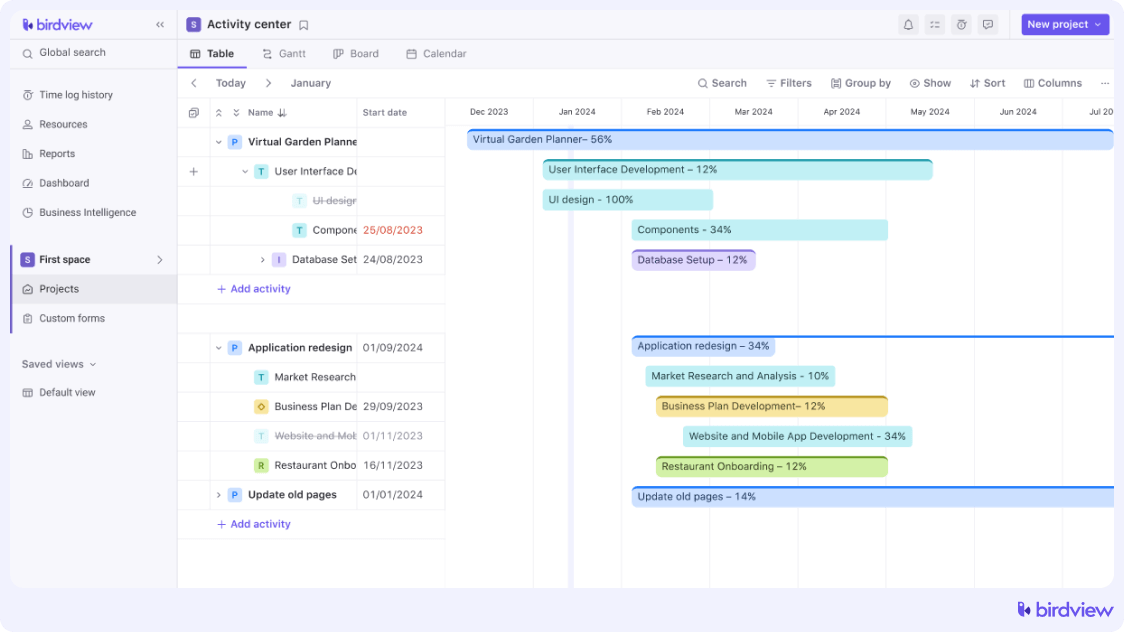
Gantt Charts
A Gantt chart maps out your project’s schedule, letting you see everything simultaneously. It breaks down each task like a point on a timeline so you can ensure everything lines up correctly, tasks don’t clash, and everyone knows what they should be doing and when.
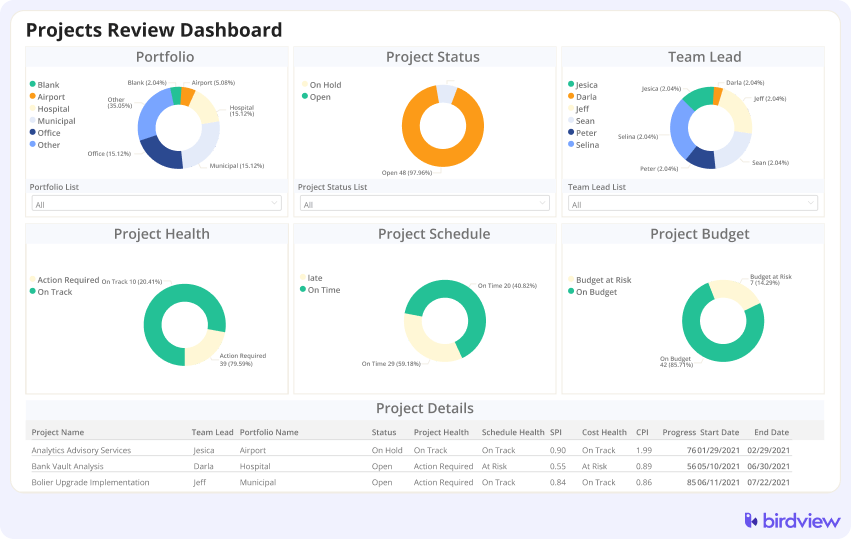
Visualize and Analyze Real-Time Data with BI Reports
BI Reports offer clarity and foresight, allowing you to navigate the project landscape precisely and confidently. Tailor your BI Reports to focus on the metrics that matter most to your project. Whether tracking financials, assessing team productivity, or monitoring timelines, you can customize your reports to provide the insights you need.
Dashboard and Reporting Tools
Your project dashboard is the control room from which you oversee the entire performance. Modern software tools offer real-time data, from task progress to resource allocation, ensuring you have the information you need to make informed decisions at your fingertips.
Reduce Risks with Artificial Intelligence
In project management, Artificial Intelligence (AI) works like an intelligent system that can spot future problems before we can, helping us avoid surprises.
AI uses past data and learning algorithms to predict and rank risks, helping you tackle them proactively before they affect your project.
Project managers choose Birdview for project Monitoring and control
Project managers often select Birdview as their go-to solution for overseeing and managing projects and portfolios due to its comprehensive features for monitoring and controlling various project aspects.




