When planning for business growth or managing a large project, one thing is clear: you can‘t succeed without the right resources. Think of it like building a house–without the right materials and tools, construction will stall, leading to delays and added costs. In project management, this is where capacity forecasting comes in. It‘s your blueprint for making sure you have the right team, skills, and tools to deliver on time and meet your business goals. Without it, you risk running into bottlenecks, missed deadlines, and lost opportunities.
Capacity forecasting isn‘t just about avoiding setbacks; it‘s about positioning your business for success. By anticipating what resources you‘ll need and when,
- you can make informed decisions,
- deliver high-quality results,
- and keep your projects on track.
💡 So, how can you perfect the art of capacity forecasting? Let‘s dive into the main strategies and best practices to future-proof your business
![]() Click here to read about the manual approach of capacity forecasting for teams.
Click here to read about the manual approach of capacity forecasting for teams.
![]() Click here to read about the automated approach of capacity forecasting for teams.
Click here to read about the automated approach of capacity forecasting for teams.
What is capacity forecasting?
Capacity forecasting estimates future workloads and identifies the resources needed to meet anticipated demand within an organization. Often referred to as resource forecasting or demand forecasting, this practice involves analyzing historical data alongside current trends.
By evaluating past performance and understanding upcoming projects, you can predict how many personnel, tools, or hours will be necessary.
Adopting this proactive approach helps businesses allocate resources proficiently, making sure that the right people and tools are available at the right time.
Eventually, capacity forecasting enables organizations to work smarter, improve operations, and better meet client expectations.
What is the difference between capacity planning and capacity forecasting?
| Factor | Capacity Planning | Capacity Forecasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Capacity planning is all about figuring out what resources you‘ll need to meet future demands. It‘s strategic and helps ensure you’re ready to handle growth or changes down the road. | Capacity forecasting, on the other hand, is more about predicting what resources you‘ll need in the near future by looking at historical data and trends. |
| Focus | The focus here is on aligning your resources with your long-term goals. It‘s about making sure your team and tools are ready for what‘s ahead. | Forecasting focuses on analyzing data to predict what‘s coming up soon, making sure you’re not caught off guard by sudden changes in demand. |
| Timeframe | Capacity planning takes both short-term and long-term strategies into account. It looks ahead to make sure you‘re covered now and in the future. | Capacity forecasting is mainly short-term. It‘s all about figuring out what you need in the immediate future. |
| Approach | It‘s a mix of reactive and proactive approaches, meaning you‘re not just planning for the future but also adjusting as things happen. | Forecasting uses a data-driven approach to pinpoint where you might run into resource shortages so you can adjust ahead of time. |
| Outcome | You get a thorough plan that ensures your operations run smoothly and efficiently. | Forecasting gives you insights into upcoming changes so you can prepare and avoid any surprises. |
What is the process of capacity forecasting? Capacity forecasting process
Here‘s an easy-to-follow guide on the capacity forecasting process, giving you practical steps to make sure your team has the right resources to meet expected demands. ![]()
1. Analyze business and resource demand
To kick off capacity forecasting that works, start by analyzing your business and resource demand.
Dive into historical data and look for trends that could affect future workloads. Check past performance metrics, seasonal shifts, and any industry-specific factors that might influence demand.
Don‘t hesitate to reach out to stakeholders for insights on upcoming projects, product launches, or market changes.
By considering both internal and external factors, you‘ll gain a clearer picture of what your team will face. Visual tools like charts and graphs can help illustrate your findings and communicate insights without any sort of communication gaps.
This analysis lays the groundwork for all the forecasting steps that follow, paving the way for a strategic approach.
2. Forecasting demand
After analyzing demand, it‘s time to forecast what‘s ahead!
Use a blend of quantitative and qualitative techniques for this task. Methods like time series analysis and regression models can project future workloads based on historical data.
Also, explore demand forecasting tools and software that can make this process more accurate.
Don‘t overlook qualitative methods, such as consulting with team members or organizing focus groups. Their insights can uncover valuable information that raw data might miss.
By merging both approaches, you‘ll create a comprehensive forecast that considers various influencing factors.
3. Look into current capacity
Once you have your demand forecast, assess your current capacity.
Take stock of your resources–personnel, equipment, and technology. Identify strengths and weaknesses in your existing setup, and see how they match up with your projected demand.
Leverage capacity management tools to map out resource availability and utilization rates.
Analyzing this data will help you understand how well your team can meet the projected demands. Look for potential resource shortfalls that could impact performance.
Knowing your current capacity enables you to make informed decisions about resource allocation and adjustments.
4. Calculate resource capacity
Next, focus on calculating how much work your current resources can handle within a specific timeframe. Break down each resource type–human, technological, and material–and assess their output capabilities.
For example, if a team member can complete ten tasks weekly, multiply that by the number of team members to find your total capacity.
Likewise, evaluate your equipment and technology to gauge their contributions.
By calculating resource capacity, you‘ll see if your existing resources are enough to meet the expected demand.
5. Measure the capacity gap
With a firm grasp on both demand and current capacity, it‘s time to measure the capacity gap.
Compare the forecasted demand with your calculated resource capacity to pinpoint any discrepancies.
If your forecast shows that demand exceeds your capacity, consider your options for bridging that gap. This might involve hiring more staff, reallocating resources, or investing in new technology.
On the flip side, if your capacity outstrips demand, think about optimizing resource utilization to avoid waste.
Catching these gaps early allows for proactive adjustments.
6. Run what-if scenarios
What-if scenarios are a fantastic way to explore different capacity planning strategies. Run simulations based on varying demand projections or resource changes to assess potential outcomes.
Think about factors like changes in project timelines, shifts in market demand, or launching new products.
Data modeling tools can help you visualize how different strategies will impact overall capacity.
Exploring these scenarios empowers your team to prepare for uncertainties and adapt to changing conditions.
7. Use a capacity planning model
Implementing a capacity planning model adds structure to your forecasting process. This framework allows you to continuously assess and adjust capacity in response to demand.
Various models are available, such as the Theory of Constraints or the Lean Manufacturing approach–each offers unique methodologies for managing capacity.
Choose a model that fits your organizational needs and operational structure. Customize it to incorporate key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your business objectives.
8. Aligning capacity with demand
The final step in your capacity forecasting journey is aligning your capacity with demand. This means positioning your resources to meet forecasted workloads.
Revisit your resource allocation strategies based on insights gathered throughout the forecasting process.
Engage with team members and stakeholders so that everyone understands the alignment between capacity and demand. This collaborative approach promotes transparency and encourages proactive problem-solving.
Keep an eye on performance and make adjustments as necessary to maintain alignment over time.
How to automate capacity forecasting? Capacity forecasting tools
Capacity forecasting can be automated using specialized tools. These tools simplify the process by offering predictive insights into resource availability, future demands, and team capacity.
Instead of manually tracking resource data and demand trends, capacity forecasting tools use algorithms to provide real-time insights and accurate projections.
Using these tools businesses can make timely, informed decisions without relying on manual data input.
What are capacity forecasting tools? What do they do? And what type of businesses should use these tools?
Capacity forecasting tools are software solutions designed to predict a team‘s ability to meet project demands. They gather and analyze data related to resource availability, workload distribution, project timelines, and skills allocation.
These tools allow businesses to visualize team workload, identify capacity gaps, and plan for future demands.
They are particularly beneficial for businesses with multiple, ongoing projects that require planned resource allocation–such as consulting firms, IT services, and project management teams.
Companies looking to optimize their workforce, avoid delays, and maximize resource utilization should consider using these tools.
How can you automate capacity forecasting using a capacity forecasting tool? Birdview PSA
Birdview PSA enables teams to track and predict resource needs based on current workloads, skill sets, and upcoming projects.
With its user-friendly interface and powerful analytics, Birdview PSA simplifies the automation process, ensuring precise capacity forecasting without manual intervention.
The tool works by letting users input project demands and resource availability into the system. It then generates predictive reports, helping decision-makers align their team’s workload with future requirements.
Step-by-step process of automating capacity forecasting with Birdview PSA
1. Input Project Data
Begin by entering key details about your ongoing and upcoming projects into Birdview PSA. Include resource requirements, timelines, and specific skills needed for each task.

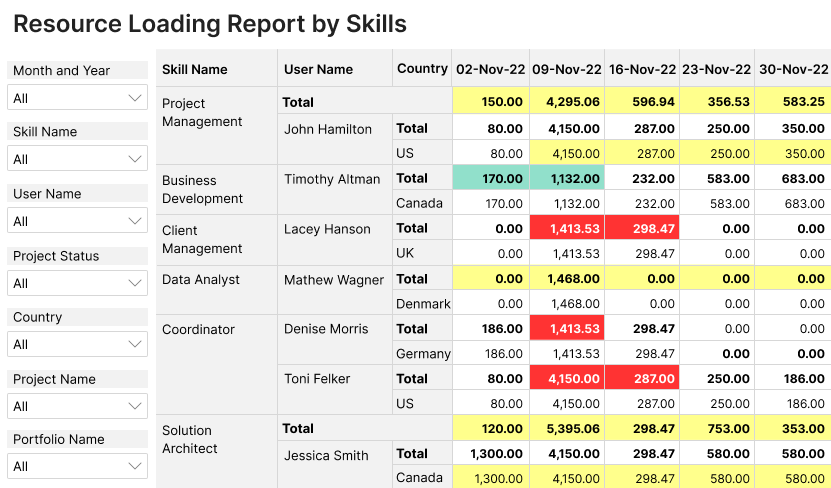
2. Review Resource Availability
Access Birdview PSA‘s visual dashboard to assess your team‘s current workload and availability. The tool offers a real-time view of how resources are distributed across various projects.
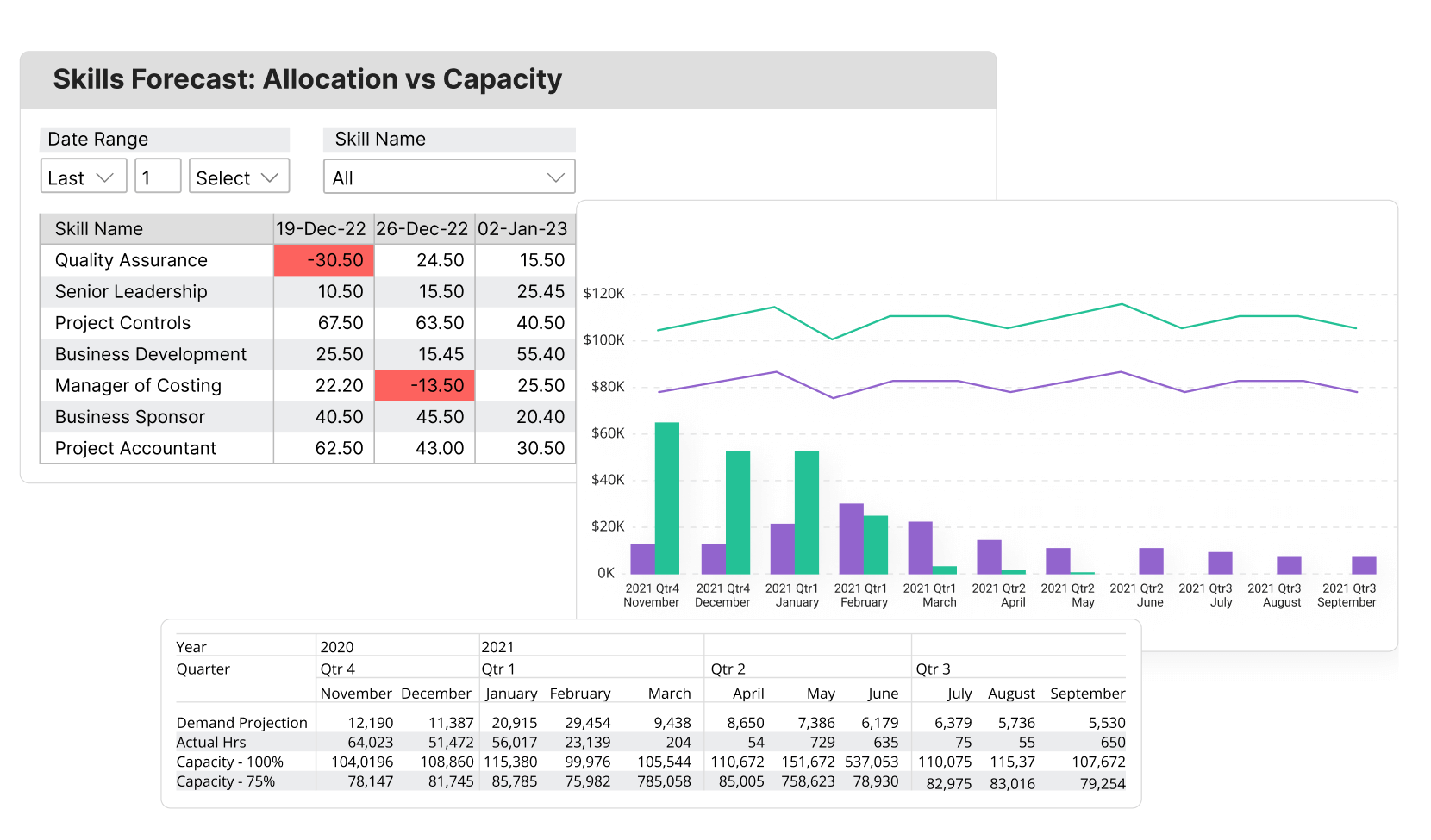
3. Forecast Future Capacity
Use the software‘s built-in forecasting feature to predict future resource needs based on the entered data. Birdview PSA uses advanced algorithms to project capacity requirements for the upcoming months.
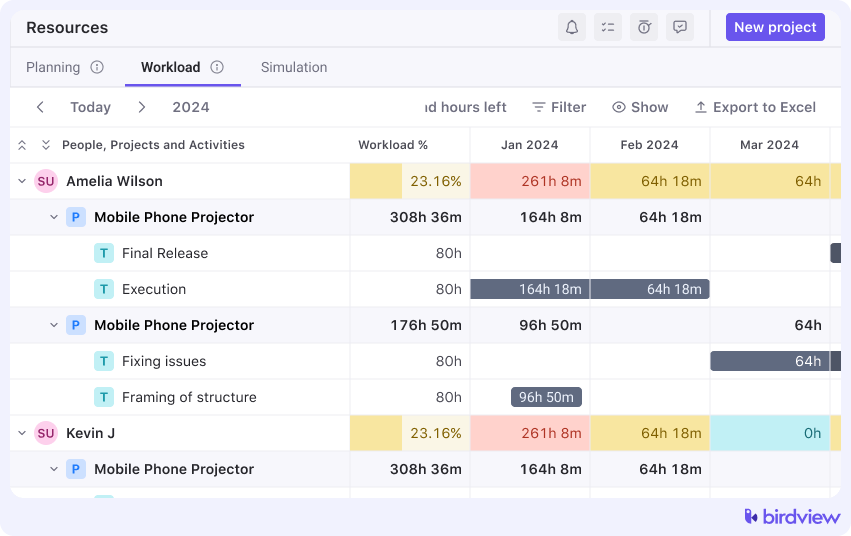
4. Adjust Workload Distribution
The system identifies underutilized or overloaded team members. Adjust workloads directly from the dashboard to ensure an even distribution of tasks and responsibilities.
5. Analyze Reports
Birdview PSA generates detailed reports that provide insight into capacity gaps, workload distribution, and resource availability. Use these reports to make informed decisions about resource planning and hiring needs.
6. Implement Decisions
Once the forecasts are reviewed, apply the necessary adjustments to your resource plan. Book resources in advance or reassign team members to balance workloads proactively.
7. Monitor and Refine
Continuously monitor your team‘s capacity with the tool‘s real-time data to adjust for changes in demand or resource availability. Birdview PSA will make sure that you stay ahead of potential bottlenecks.
Manual forecasting relies on static data and human input, which can lead to errors and time-consuming updates. In contrast, automated tools use real-time data and advanced analytics to deliver up-to-date insights without manual intervention.
Birdview PSA online user reviews
As of the writing date, Birdview PSA has 4.5 out of 5 stars and 367 reviews on Capterra.
Here‘s what some of Birdview PSA‘s users have to say about their product.
Derek E., found Birdview to be an exceptional tool for managing Professional Services Projects. After using the software for 1-2 years, Derek rated it 5.0 across all aspects, including ease of use, customer service, features, and value for money, and gave it a 10/10 likelihood to recommend.
Liz T., a Manager in the E-Learning industry, found Birdview to be flexible enough to cater to individual workflows and thinking styles. After using the software for 6-12 months, Liz rated it 5 out of 5 overall. Liz highlighted that Birdview’s powerful modular approach allows for flexible usage but can also present challenges for those who prefer stricter parameters.
Dawood H., a Fund Services Manager in a company with over 10,001 employees, found Birdview to be a simple and intuitive tool. He praised the software for its ease of use, particularly highlighting how Birdview simplifies time recording, a task most people dislike. He also appreciated the feature that allows users to roll over their time data each week.
Try BirdviewPSA for free
If you feel that Birdview PSA might be the right capacity forecasting tool for your business, sign up to start using Birdview PSA for a 14-day trial or book a demo. If you need any help with your Birdview PSA subscription or want to better understand our pricing, please navigate to our support center here.
Different types of capacity forecasting
Here are the different types of capacity forecasting (you should be familiar with) that can help your business manage resources and meet demands ![]()
1. Qualitative Forecasting
Qualitative forecasting relies on expert judgment, market research, and surveys to estimate capacity needs. It‘s particularly useful when historical data is limited or unavailable.
The process typically involves gathering insights from experienced personnel, industry analysts, or focus groups to make informed predictions.
![]() Example: A tech company may consult industry experts to gauge future demand for a new product line, using their insights to forecast the required production capacity.
Example: A tech company may consult industry experts to gauge future demand for a new product line, using their insights to forecast the required production capacity.
2. Quantitative Forecasting
Quantitative forecasting uses statistical methods and historical data to predict future capacity requirements. Techniques like time series analysis and regression analysis analyze past trends to make data-driven projections.
The process involves collecting data, identifying patterns, and applying mathematical models to forecast future needs.
![]() Example: A manufacturing firm analyzes sales data from the past five years to predict future production levels based on seasonal trends.
Example: A manufacturing firm analyzes sales data from the past five years to predict future production levels based on seasonal trends.
3. Bottom-Up Forecasting
Bottom-up forecasting gathers data from individual departments or teams to create an overall capacity forecast. This approach emphasizes the insights of those directly involved in operations.
The process starts with departmental inputs, which are then aggregated to form a complete forecast.
![]() Example: A retail chain collects input from store managers about expected sales and inventory needs to forecast overall staffing and stocking requirements.
Example: A retail chain collects input from store managers about expected sales and inventory needs to forecast overall staffing and stocking requirements.
4. Top-Down Forecasting
Top-down forecasting begins with high-level organizational goals and breaks them down into specific capacity needs. It typically involves executive decisions influenced by market analysis and strategic objectives.
The process starts at the organizational level, filtering down to departments.
![]() Example: A large corporation decides to expand its product line and directs each division to estimate the capacity required to meet new sales targets.
Example: A large corporation decides to expand its product line and directs each division to estimate the capacity required to meet new sales targets.
5. Scenario Forecasting
Scenario forecasting evaluates various potential future scenarios to assess their impact on capacity requirements. This approach considers different variables, such as market changes or economic shifts.
The process involves developing multiple scenarios and analyzing how each might affect capacity.
![]() Example: A logistics company creates scenarios for varying fuel prices to understand how these fluctuations could affect their delivery capacity.
Example: A logistics company creates scenarios for varying fuel prices to understand how these fluctuations could affect their delivery capacity.
6. Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting focuses specifically on predicting customer demand, which directly influences capacity planning.
The process involves analyzing market trends, customer behaviors, and external factors to anticipate future sales and service needs.
![]() Example: An e-commerce business uses past sales data and market trends to project demand during holiday seasons, helping them prepare adequate inventory.
Example: An e-commerce business uses past sales data and market trends to project demand during holiday seasons, helping them prepare adequate inventory.
7. Resource-Based Forecasting
Resource-based forecasting considers the availability and utilization of resources, such as labor and equipment, to determine capacity needs. This method assesses how efficiently existing resources can meet projected demand.
The process involves analyzing resource constraints and potential bottlenecks.
![]() Example: A construction firm evaluates its workforce and machinery availability to ensure it can handle projected projects over the coming year.
Example: A construction firm evaluates its workforce and machinery availability to ensure it can handle projected projects over the coming year.
8. Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP)
S&OP is an integrated method that aligns demand forecasts with supply capabilities. It combines insights from sales, marketing, production, and finance to create a unified capacity plan.
The process involves regular meetings and collaboration among departments to ensure alignment with business goals.
![]() Example: A beverage company uses S&OP to align sales forecasts with production schedules, ensuring that they can meet customer demand while optimizing resource use.
Example: A beverage company uses S&OP to align sales forecasts with production schedules, ensuring that they can meet customer demand while optimizing resource use.
What is the importance & benefits of capacity forecasting?
You can never underestimate the importance and benefits of practicing capacity forecasting, and here‘s why ![]()
1. You Can Easily Avoid Bottlenecks
Spotting potential resource issues early is necessary for keeping projects on track. When you assess your team‘s capacity, you can identify where constraints might pop up before they lead to major delays.
By doing this, you can make adjustments–whether it’s reallocating tasks or bringing in extra help.
With fewer bottlenecks, your team can stay focused and keep moving forward, making for a smoother project lifecycle.
2. More Time To Plan for Business Growth
Capacity forecasting helps you anticipate future resource needs. Knowing when and where you might need extra support lets you proactively scale your team and invest in the right tools.
This foresight is invaluable; it means your business is ready to seize new opportunities without stretching current resources too thin.
When growth comes knocking, you‘ll be prepared to welcome it.
3. You Can Avoid Unnecessary Project Delays By Simplifying Resource Allocation
Making informed decisions about resource distribution assures that the right resources are available at the right time to meet project timelines. When you have a clear understanding of your team‘s strengths and project needs, you can proactively allocate resources.
This not only leads to efficient staffing but also reduces the risk of project delays, enhancing your credibility with clients.
A streamlined approach like this creates a more productive environment where everyone can focus on their tasks, eventually leading to project success.
4. You Become More Proactive At Problem-Solving
Regularly checking your resource allocation helps you catch potential issues before they grow. For example, if a team member seems overloaded, you can easily redistribute tasks to keep things balanced.
This proactive mindset minimizes disruptions, allowing your team to stay effective.
By addressing challenges early, you promote a flexible team that can handle unexpected changes with confidence.
5. Helps You Make Data-Driven Hiring Decisions
Strong data on capacity needs is key to justifying new hires. Clear insights into your team‘s requirements make it easier to argue for additional staff.
Using a data-driven approach not only strengthens your case but also makes sure you hire strategically, bringing in the right talent at the right time. The result? A more capable team ready to tackle challenges head-on.
6. Eliminate Waste and Reduce Operational Costs Before It‘s Too Late
Identifying inefficiencies allows you to optimize resource use and make informed decisions to reduce unnecessary expenses. Whether it’s underused or overstaffed resources, making smart adjustments guarantees that everyone’s skills are fully utilized.
This proactive approach enhances productivity and cuts down on wasteful spending. As a result, you can allocate your budget more effectively, invest in growth-promoting areas, and improve service delivery.
7. Promotes The Cultures of Transparency and Accountability
Providing clear insights into resource allocation promotes a culture of transparency and accountability. Everyone understands their role and what‘s expected of them.
This clarity encourages teamwork and open communication, making collaboration easier. When everyone is aligned, the team operates more smoothly.
8. Helps You In Delivering Projects on Time & In Budget
Aligning resources with project timelines and budgets is vital for success. Perfectly executed capacity forecasting makes sure you have the necessary resources ready when you need them.
This alignment not only helps you deliver projects on time but also keeps costs in check.
Clients appreciate timely delivery and sticking to budgets, leading to repeat business and positive referrals.
9. Increased Employee Motivation & Retention
Keeping workloads balanced is key to preventing burnout. When you forecast capacity, you can make sure that no one is overwhelmed.
A manageable workload leads to higher job satisfaction and promotes a positive environment where employees feel valued. This not only keeps your team motivated but also reduces turnover, saving you time and money on recruitment and training.
10. Helps In Managing Skills and Uncover Hiring Needs
Capacity forecasting helps you gauge your team‘s current skills and pinpoint any gaps. By knowing where your team shines and where they need support, you can assign tasks more proactively.
Furthermore, this insight helps you uncover hiring needs, making sure you bring in the right talent to fill those gaps.
What are the elements included in capacity forecasting? Forecasting capacity requirements
Capacity forecasting involves several key elements that help organizations predict and plan their resource needs. Here are some of the below ![]()
| Element | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Demand Forecasting | Analyze past sales and market trends to predict future customer needs. Consider seasonal changes and how customers behave. |
| Resource Analysis | Evaluate your current resources, like staff and equipment, to understand what you have available. |
| Bottleneck Identification | Identify problems in your production process that could slow things down and limit capacity. |
| Scalability Assessment | Check how easily your systems can adjust to changing demand–can they expand or shrink quickly? |
| Cost Considerations | Think about the costs of increasing or decreasing capacity, both in the short and long term. |
| Market Trends Analysis | Keep an eye on industry trends and changes that could affect demand. |
| Seasonal Variations | Plan for demand changes that happen at different times of the year, like holidays. |
| Technology Evaluation | Assess if you need new technology or upgrades to improve efficiency and capacity. |
| Capacity Planning Strategies | Decide on approaches to manage capacity–whether to prepare in advance, react, or match demand. |
Capacity forecasting examples
Here are a few practical examples of capacity forecasting ![]()
1. Marketing Campaign Launch
Problem: When launching a marketing campaign, teams often struggle with resource allocation.
They might overestimate capacity or assign too few resources, which leads to missed deadlines and underperformance.
Marketing efforts demand a careful balance between creativity, execution, and tracking, yet it‘s easy for work to bottleneck during critical moments.
Solution: Capacity forecasting helps marketers anticipate their team’s workload and allocate resources in planned fashion.
By reviewing historical data from previous campaigns, teams can estimate the amount of work required for each task, such as content creation, design, and analytics.
With capacity forecasting tools, you can map out the entire campaign, identify gaps in resourcing early, and adjust before execution. Following this step-by-step breakdown of capacity forecasting, the campaign managers will make sure that no stage of the campaign suffers from over- or under-utilization, providing a smooth launch process.
2. Product Development
Problem: Product development teams frequently face delays due to poor resource planning. Without a clear understanding of team capacity, projects can drag out, causing missed deadlines and extra costs.
Complex projects often require a blend of design, development, and testing, with each phase relying on a well-distributed workload.
Solution: Capacity forecasting allows product managers to visualize the workload across all stages of development.
By using historical data and analyzing current capacity, they can estimate how long each development phase will take, from design through testing.
Forecasting tools enable you to balance workload among team members, prevent burnout, and ensure every team has the resources to meet critical milestones.
A step-by-step approach to forecasting during each product phase ensures timely delivery and keeps your team agile throughout the project.
3. Seasonal Sales Surge
Problem: Retail and e-commerce companies often experience seasonal spikes in demand. Without proper planning, these surges can overwhelm teams, leading to stockouts, delayed orders, and frustrated customers.
Balancing operational demands during peak times becomes a major challenge, especially when resources are limited.
Solution: Forecasting capacity for seasonal demand makes sure your team is prepared for fluctuating workloads. Analyzing past performance data during peak periods helps predict staffing and production needs.
Capacity forecasting tools allow you to automate the process of scheduling and resource allocation, so that you have the right number of employees or stock levels to manage the surge.
This proactive approach prevents overburdening your team and enhances customer satisfaction by keeping operations running smoothly during high-demand periods.
4. Client Projects
Problem: Managing multiple client projects at once can create chaos if teams are overstretched. A lack of insight into available capacity often results in missed deadlines, overworked staff, and dissatisfied clients.
Balancing priorities becomes even more difficult when juggling several projects simultaneously.
Solution: Capacity forecasting provides clarity into your team’s workload, making it easier to allocate resources based on each project’s priority.
By using a capacity forecasting tool, project managers can input data about current projects and team availability to generate a detailed overview of capacity. This helps distribute tasks evenly across the team so that every project gets the attention it deserves.
5. Service Expansion
Problem: Expanding services while managing existing operations presents a logistical challenge.
Businesses often miscalculate how much additional workload their team can handle, leading to resource strain, reduced service quality, and inefficient scaling.
Solution: Capacity forecasting helps businesses plan for growth by evaluating the current workload and predicting the resources needed for new services.
Using forecasting tools, you can simulate different expansion scenarios, allowing for more accurate hiring, equipment purchases, and task distribution. This process makes your team remain capable of handling the existing workload while integrating new services.
As a result, you can grow your business without overwhelming your team or compromising service delivery.
Capacity forecasting strategies, tips, & best practices
Here are some of the best practices and tips you can follow if you want to practice capacity forecasting in your business.
| Tips & Best Practices | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Analyze Historical Data | Look at past sales and customer demand to find patterns that can help predict future needs. |
| Use Advanced Analytics | Use data analysis tools to create different scenarios and get better predictions for capacity needs. |
| Engage Stakeholders | Involve key team members from sales, marketing, and operations to gather various insights. |
| Monitor Market Trends | Keep up with industry trends, competitor actions, and economic changes that could affect demand. |
| Implement Demand Forecasting Software | Use specialized software to automate data collection and analysis for easier forecasting. |
| Review and Adjust Regularly | Set a routine to check forecasts and make changes based on new data or unexpected demand shifts. |
| Train Your Team | Provide training for staff involved in forecasting so they know how to use the tools and methods. |
| Create Multiple Scenarios | Plan for different possibilities by developing best-case, worst-case, and most likely scenarios. |
| Use Cross-Department Collaboration | Encourage communication between departments to align forecasts with overall business goals. |
| Evaluate External Factors | Consider outside influences like economic conditions and regulations that could impact demand. |
| Focus on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Track important metrics, like lead times and inventory turnover, to measure forecasting accuracy. |
| Document Assumptions | Write down the assumptions made during forecasting to ensure transparency and accountability. |
| Use Rolling Forecasts | Continuously update your forecasts based on the latest information available. |
| Review Capacity Against Goals | Regularly compare your forecasts to business goals to make sure you‘re ready for growth. |
| Prepare for Variability | Build flexibility into your plans to handle unexpected changes in demand. |
Now that you have a thorough understanding of the tips and best practices, let‘s dive into strategies for forecasting capacity.
When it comes to capacity planning, the right strategy can make all the difference for your business.
Let‘s break down some common approaches: Lead, Lag, Match, Adjustment, and Hybrid strategies. Each one has its unique strengths, so the key is finding what works best for your situation.
1. Lead Strategy
The lead strategy is all about being proactive. You increase your capacity before demand hits, making sure you‘re ready to go when customers come calling. This means staying on top of market trends and understanding your resources inside and out.
Imagine a holiday decoration company gearing up for the festive season. They might ramp up inventory and hire extra staff well in advance, knowing that demand will spike.
When done right, this strategy can increase customer satisfaction and grow market share. Just remember: if you overestimate demand, you could end up with excess inventory and increased costs.
2. Lag Strategy
On the other hand, we have the lag strategy. This approach is reactive–you expand your capacity only after demand surpasses what you can handle. It can save money in the short term, but it risks disappointing customers in the long run.
Think about a tech support firm. They might wait until customer calls flood in before hiring more technicians or relying on overtime. If a sudden spike in demand occurs, clients might face long wait times, which can hurt the company‘s reputation.
3. Match Strategy
Next up is the match strategy, which strikes a balance between lead and lag. You gradually increase capacity to keep pace with demand. Adopting this method helps you minimize risks, but it can be tricky in industries with unpredictable demand, like event planning.
For example, an event management company might adjust staffing based on client bookings. By regularly monitoring how many events are scheduled, they can optimize their team and resources, making sure they‘re efficient and cost-effective.
4. Adjustment Strategy
The adjustment strategy focuses on quick, short-term changes to meet demand. It often involves hiring part-time workers or freelancers during peak times. While it offers flexibility, it can also introduce challenges like inconsistent quality or mistakes from less experienced staff.
To make this work, you must have a solid onboarding process for temporary workers. For instance, a restaurant can provide thorough training for seasonal staff to ensure they deliver top-notch service during busy dinner shifts.
5. Hybrid Strategy
A hybrid strategy blends elements from all these approaches, giving you flexibility and balance.
For instance, a retail store might ramp up staffing before the holiday season (lead), cut back after the rush (lag), and find a steady level during quieter months (match).
The following strategy needs flexibility and good planning, but it helps you adjust quickly to changes in the market. Keep an eye on what‘s working and be ready to make changes when necessary.
Scenario Planning
Finally, let‘s talk about scenario planning. This is important for implementing a hybrid strategy proactively.
It helps you prepare for different demand outcomes by creating flexible plans that can adapt to various situations.
Moreover, this is especially helpful in uncertain markets, where being prepared can set you apart from the competition.
Yes, scenario planning can be complex and take time, but it makes sure you‘re ready for whatever comes your way. With a little foresight, you can build a resilient business that thrives no matter what the future holds.
Common capacity forecasting mistakes and challenges for teams
Capacity forecasting is a critical task for businesses, but it’s easy to make mistakes or encounter challenges that can throw off your planning.
One common mistake is relying too heavily on historical data without considering current market trends or changes. This narrow focus often leads to inaccurate predictions and resource shortages.
Similarly, neglecting to involve team members in the forecasting process misses out on valuable insights into workload fluctuations.
Another challenge businesses face is the unpredictability of project timelines. When a project runs longer than expected, it can disrupt capacity plans, causing delays for multiple teams.
Balancing current workloads while preparing for future projects is tricky, and overcommitting resources can lead to burnout and missed deadlines.
Accurate data is key. Without clear insights into team availability and project requirements, businesses are prone to faulty assumptions that create inefficiencies.
Additionally, failing to account for unexpected events–like sudden shifts in demand, project delays, or changing client needs–requires quick adjustments to forecasts to stay on track.
Lastly, many organizations overlook the importance of regular reviews and adjustments to forecasts. Conditions change, and being flexible is essential.
It’s also important to balance both quantitative data (like resource availability) and qualitative factors (like employee morale or client feedback) for more accurate capacity planning.
Capacity forecasting vs. resource forecasting: what‘s the difference?
| Aspect | Capacity Forecasting | Resource Forecasting |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Look at the total capacity available for the team or resources. | Looks at the specific skills, roles, and people needed for tasks. |
| Objective | Makes sure that future demand can be met with available resources. | Assigns the right people to tasks based on their skills and roles. |
| Scope | Considers overall workload, current and future projects, and availability. | Focuses on individual team members‘ workloads, skills, and time. |
| Typical Use Case | Check if there‘s enough capacity for upcoming projects. | Allocates individuals to projects based on their availability and skills. |
| Example | A team of 10 can work 400 hours per week. | A senior developer is needed for 50 hours over two weeks. |
| Granularity | Looks at total team or resource availability. | Focuses on specific individuals, roles, and skills. |
| Purpose | Make sure there is enough overall capacity for future work. | Ensures the right resources are assigned to tasks or projects. |
| Timeframe | It provides a broad view, typically covering weeks or months. | Deals with task-specific, immediate, or short-term planning. |
FAQs
What is forecasting and capacity planning in operations management?
In operations management, forecasting covers the process of estimating future demand for a product or service based on historical data and market trends.
Whereas, capacity planning determines the production capacity needed to meet expected demand for goods or services.
What should you look for in a capacity planning tool?
When choosing a capacity planning tool, you want something that fits your team‘s needs. Here‘s what to keep in mind ![]()
- User-friendly interface for easy navigation
- Real-time data integration with existing systems
- Strong forecasting capabilities
- Scenario planning for simulating situations
- Efficient resource allocation for managing workloads
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics
- Collaboration features for enhanced teamwork
- Scalability to grow with your business
- Customization options for specific workflows
- Cost-effectiveness to make sure value is within your budget
Can you forecast resource demand?
Absolutely, you can forecast resource demand!
This involves analyzing current and historical data to predict future needs for resources such as staff, equipment, and materials.
You can create accurate predictions by looking at trends, understanding demand drivers, using various forecasting methods, and incorporating flexibility.
Utilizing resource management tools like Birdview can also help you visualize and adjust your forecasts as needed. Regularly reviewing your actual usage against your forecasts will keep your planning on track.
Is it hard to forecast capacity?
Yes, forecasting capacity can be difficult.
Factors that contribute to this difficulty include:
- uncertainties from unexpected events,
- data limitations due to inaccuracies,
- lack of visibility when information is scattered,
- inflexible tools like spreadsheets,
- multiple production timelines that complicate data aggregation,
- and employee churn that can disrupt staffing.
All these elements make it tough to predict capacity accurately.
Who is responsible for capacity forecasting?
The resource manager is the main person responsible for capacity forecasting. They focus on understanding what resources are needed for upcoming projects and making sure they are available when required.
Their job is to manage and allocate resources proactively, helping the organization meet its goals and keep projects on track.
Final say
Mastering capacity forecasting is key to aligning your team‘s resources with project demands. By evaluating past performance and pinpointing capacity gaps, you can allocate resources more proactively and avoid overburdening your staff.
Birdview PSA makes this process easier by offering real-time insights and predictive analytics. Its user-friendly interface helps you adjust plans quickly, making sure your team is always prepared for what‘s next.
With Birdview PSA, you can turn capacity forecasting into a powerful tool for your business, helping you navigate uncertainties and drive success.



