If you‘re looking to manage projects, understanding the nuances of project management is critical to completing projects on time and within budget. But what exactly does project management involve? What are its stages, key methods, and practices? How can you choose the right project management software that best suits your needs?
Our comprehensive guide to project management will help you answer these questions and teach you how to successfully manage a project, from planning to execution, delivery, and reporting.
What is a project?
A project is a unique task that has a beginning and an end. It is undertaken to create something new or achieve a specific goal, such as constructing a building, developing a new software product, or organizing a team meeting. Projects differ from routine work in that they have a definitive endpoint. Projects require a skilled team that can plan and execute the work, utilizing a range of skills and tools to complete it.
Projects are often temporary efforts with a defined scope, budget, and timeline. Unlike business operations, which are ongoing and repetitive, projects focus on specific outcomes and typically require cross-functional collaboration. Each project also carries some level of risk and uncertainty, which further distinguishes it from regular business activities.
What does project management mean?
Project management is the planning, organizing, and managing of a project to achieve its objectives. It begins with setting clear goals and then devising a plan to meet them. This involves determining the scope of work, the budget, and the timeline. It is crucial to outline the tasks to be completed, assign responsibilities, and set deadlines.
Project managers monitor progress to ensure that the project stays on schedule, within budget, and meets its deadlines. This includes coordinating teams, managing communication with stakeholders, and responding to risks and changes along the way. A good project manager also ensures quality deliverables and fosters a collaborative team culture throughout the project lifecycle.
Project management vs project portfolio management
Project Management centers on executing single projects by planning, organizing, and managing resources to meet specific goals on time, within budget, and at the desired quality level.
Project Portfolio Management (PPM) manages multiple projects, aligning them with business objectives and strategies. PPM prioritizes and optimally allocates resources across the portfolio, evaluating each project’s risk and potential return.
5 phases of project management life cycle
The project management process most often consists of five phases that all projects must go through. For professional services projects, there may be additional phases. Let’s look at each of these 5 phases: Project Initiation, Project Planning, Project Execution and Delivery, Project Monitoring and Control, and Project Closure.
1. Project initiation phase
The project initiation phase marks the beginning of the project. It sets the stage for everything that follows.
First, you define the project‘s purpose and objectives. Then, you assess the project‘s feasibility by checking whether you have enough time, money, and the right resources. The next step is to prepare a project charter, a document that officially starts the project. It outlines the project‘s scope, participants, and their roles, ensuring the project has a clear goal and everyone knows their next steps
2. Project planning phase
In the project planning phase, you create the project‘s roadmap, outlining a detailed plan from start to finish.
This phase involves breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks and establishing a timeline to ensure everything stays on schedule. Budgeting is also crucial at this stage, as it involves estimating the financial resources required for the project. Additionally, team roles are assigned based on the members‘ skills.
Risk management plans, communication strategies, procurement needs, and stakeholder engagement plans are also developed during this phase.
3. Project execution and delivery phase
This phase involves putting the project plan into action. The project team starts working on the outlined tasks, utilizing all resources as planned.
The project manager oversees task completion and adherence to the schedule, ensuring all work meets the project‘s standards. Regular updates are provided to stakeholders about the project‘s progress and any significant developments.
This phase also includes team coordination, managing expectations, resolving conflicts, and adapting to changes. Deliverables are produced and reviewed continuously for quality.
4. Project monitoring and control phase
This phase is essential for ensuring the project stays on track. The project manager and team compare actual performance against the plan, monitoring progress and the budget to identify any deviations early on.
Various project management reports are used, including updates on progress, timelines, team workload, and project costs. If any issues arise, the team devises solutions, potentially adjusting the plan to maintain smooth progress. Regular updates keep all participants informed about the project‘s status.
Monitoring tools such as KPIs, earned value analysis (EVA), burndown charts, and dashboards help project managers make data-driven decisions.
5. Project closure phase
The closure phase is critical for formally concluding the project, reflecting on the experience, and acknowledging the team‘s efforts.
It involves presenting the final deliverables to stakeholders, releasing resources, completing documentation, and obtaining sign-offs. This phase is also an opportunity to recognize the team‘s hard work and celebrate the project‘s success.
A post-project review, lessons learned meeting, and final report are created to evaluate performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure smooth transitions for support or next steps.
Top project management methodologies and how to choose
Like history, projects have a beginning, middle, and end. Understanding this is important for planning a successful project. One particular area that often confuses new project managers is choosing the right project management methodology. Projects come in all shapes and sizes, so when it comes to choosing a methodology for success, it’s important to know your options. In this section, we will look at the most popular project management methodologies such as Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban, and much more. Let’s list the pros and cons of each type.
Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall methodologies are the most common way to organize a project to define a sequential order for completing tasks. “A” leads to “B”, which leads to “C”. Ultimately, they all add up to the final result. Quite simple.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
The critical path method is similar to the waterfall method, however it recognizes dependencies. A dependency is a task that must be completed before another task can move forward. One task is dependent on another. This creates a critical path.
PMBOK Method
The PMBOK method is the overall process of a project. It has been accepted as an industry standard because of its roots in PMI (Project Management Institute). This method is also sequential and is focused on planning a project in five steps: Initiation, Planning, Execution, Controlling, and Closing.
Agile Methodologies
What is Agile Project Management? Agile was first introduced to the world in 2001 through the Agile Manifesto. As you may have guessed, this is a platform for software developers. There are four basic rules of Agile:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools;
- Working software over comprehensive documentation;
- Client collaboration over contract negotiation;
- Responding to change over following a plan.
The one that differentiates the agile approach is responding to change rather than following a set path. Agile is adaptive, just like the world of software development.
Scrum methodology
What is Scrum? Scrum is an agile process used most often by development teams because it is really easy to implement. One individual called the Scrum Master, is responsible for making sure that any bottlenecks or obstacles are cleared for the team for smooth project sailing. Scrum works in two-week sprints and allows for the team to be flexible with priorities.
Kanban methodology
Project Management Methodology Kanban is a Japanese framework for agile. It started in the late 40s by the car manufacturer, Toyota, as a way to make production much more efficient. Kanban is a visual representation of a project, making it easy for teams to know when something is ready for them to work on.
PRINCE2 (Projects in a Controlled Environment)
This is another methodology that you may come across quite often because it is the most commonly used around the world as it is designed to be suited to any project in any industry. Created by the UK government in 1989, it is also the most strict project management methodology out there. PRINCE2 emphasizes working in sprints, but instead of breaking down a project into small sprints, it breaks it down into a few large parts and treats every part as a sprint.
What does a project manager do?
The role of a project manager is complex and encompasses the comprehensive management of a project from its inception to its closure. This involves various responsibilities to ensure the project achieves its objectives while adhering to budget, time constraints, and quality standards. In managing service projects, such as IT services, consulting, or marketing campaigns, the role becomes even more nuanced due to the intangible nature of the outputs and the critical importance of client relationships. Here‘s a more detailed look at the project manager’s role with detailed models of service project management:
Strategic Planning
Responsibility: Define the project’s scope and objectives in collaboration with stakeholders and clients to ensure clarity and alignment of expectations.
Example: As part of the project delivery process for an IT service project involving installing new software for a client, the project manager must define the technical requirements, establish a timeline for implementation, identify key milestones, and organize training sessions for end-users.
Resource Allocation
Responsibility: Specify and assign the resources, including personnel, technology, and budgets, required to achieve project objectives efficiently.
Example: In a consulting project, this might mean assigning analysts, consultants, and subject matter experts based on their expertise while managing the budget.
Communication Management
Responsibility: Ensure consistent and transparent communication with all stakeholders, including team members and clients, to keep everyone well-informed and involved during the project.
Example: Keep the client frequently informed about the developments in a marketing campaign, respond to any issues they raise, and tweak the campaign based on their feedback.
Quality Assurance
Responsibility: Guarantee that the delivered service adheres to or surpasses the quality benchmarks set with the client.
Example: A software implementation project entails conducting extensive testing rounds to identify and fix any problems before the official launch, ensuring the software operates smoothly and does not interfere with the client’s business activities.
Risk Management
Responsibility: Actively detect potential threats and create strategies to reduce their influence on the project’s success.
Example: In an IT project, recognize the potential for data loss and establish comprehensive data backup systems and cybersecurity protocols to protect data integrity.
Client Relationship Management
Responsibility: Build and maintain strong relationships with clients, understand their needs, and adjust project details to meet these requirements better.
Example: A business consulting project might involve adapting the project scope to address emerging client needs or industry changes, thereby ensuring the consultancy provides relevant and timely advice.
Problem-Solving
Responsibility: Address and resolve issues that arise during the project efficiently to prevent them from affecting project outcomes.
Example: Quickly resolving conflicts within the project team or between the team and the client to maintain harmony and productivity.
Project Closure and Review
Responsibility: Successfully close projects, ensuring all objectives are met, deliverables are handed over, and feedback is collected to improve future project executions.
Example: At the end of a project, develop a customer service training program, ensure all materials are delivered, train staff, and conduct a post-implementation review to assess the impact of training on customer satisfaction.
In service project management, where outcomes are often directly tied to client satisfaction and the intangible nature of services, the project manager‘s role becomes crucial in ensuring the seamless integration of all these elements. This integration provides not only the delivery of the service but also the strengthening of client relationships, which is critical for long-term business success.
What tool can assist in project management?
Project management software is a tool that helps plan, organize, and manage projects, tasks, resources, and budgets.
How to choose project management software for your company or team? What features should it have to provide all the needs for managing your projects? Answering these questions is not easy. The project manager, together with stakeholders, decides which of the many project management tools is right for your company. There are many products on the market offering solutions for project management such as Microsoft Project, Monday, etc.
Birdview PSA includes essential features like project planning, resource allocation, budget management, and overseeing multiple projects in a portfolio.
Essential features of project management software
There is a wide range of project management tools, both online and mobile, available to manage projects. These are the most essential tools for a project manager:
Different views for different purposes
For effective management, every project manager should have access to a variety of tools for working with projects. This toolkit should encompass table views, Gantt charts, calendars, and Kanban boards. In Birdview, the Activity Center serves as a central hub that unifies all these views, providing a comprehensive suite of options for managing projects efficiently.
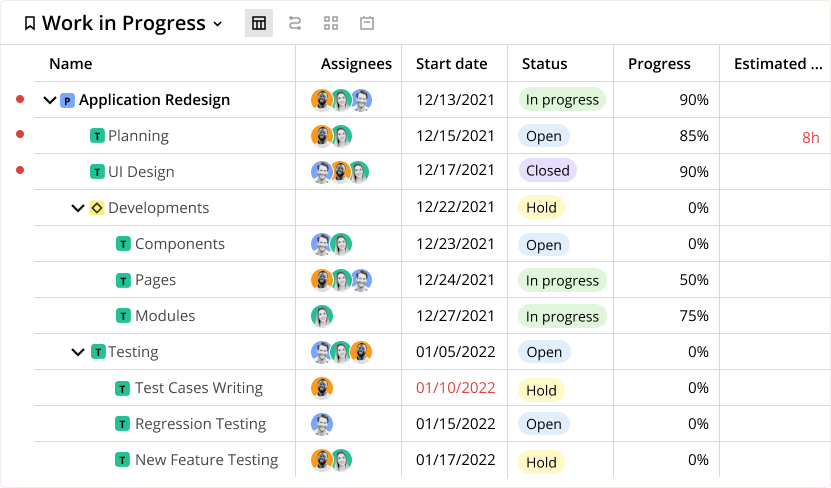
Table view
Easily create and view projects and tasks in Excel format. Assign staff to tasks and form teams. Drag and drop an unlimited number of tasks and subtasks.
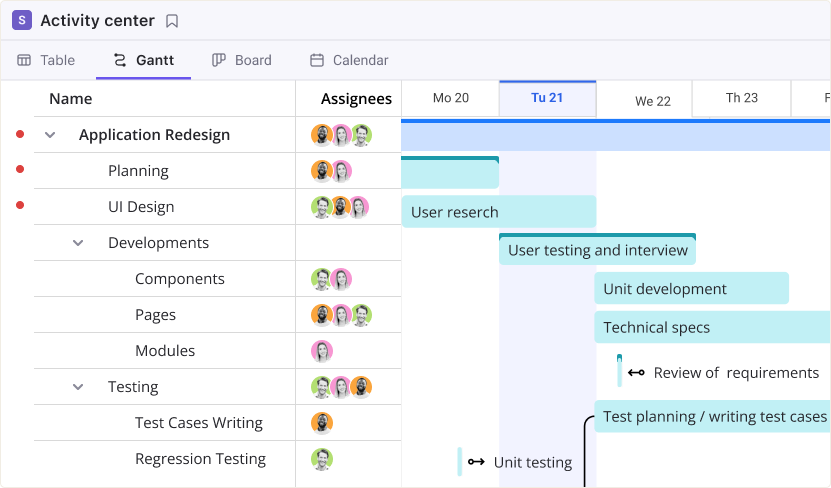
Gantt chart view
Interactive Gantt charts are designed for effective project planning, visualization of work, project scheduling, task management, and much more
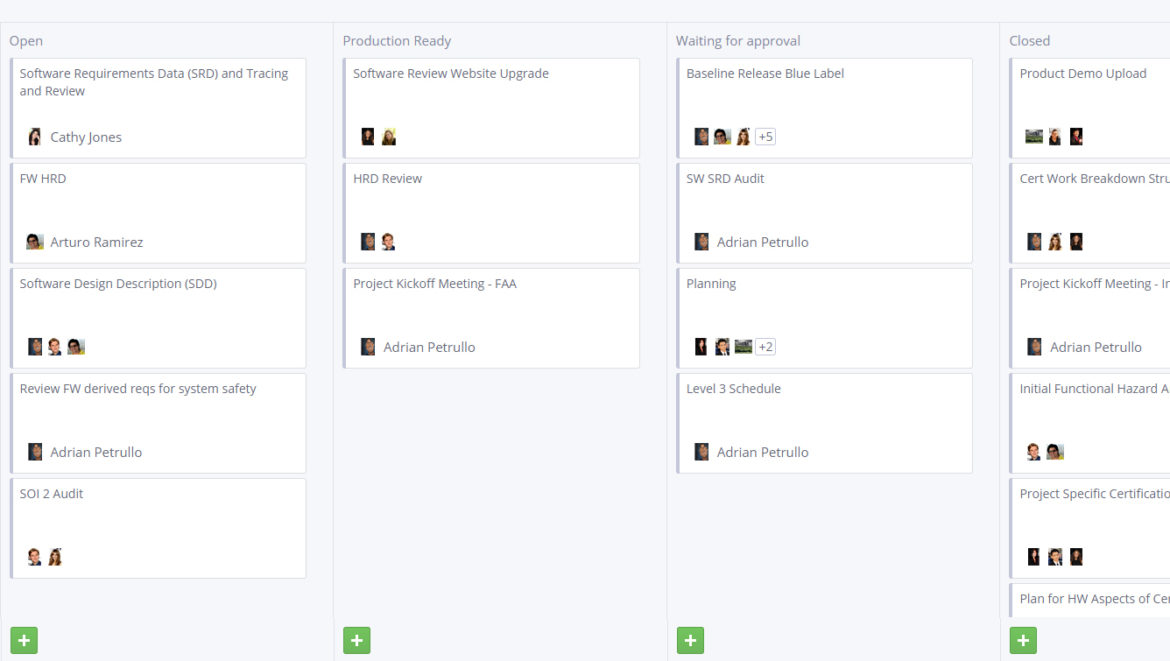
Kanban board
A Kanban-style task management makes it easy to identify bottlenecks and focus on more important things first. Kanban boards are used by Agile and Scrum teams and provide complete visibility into your team’s progress and priorities across the organization.
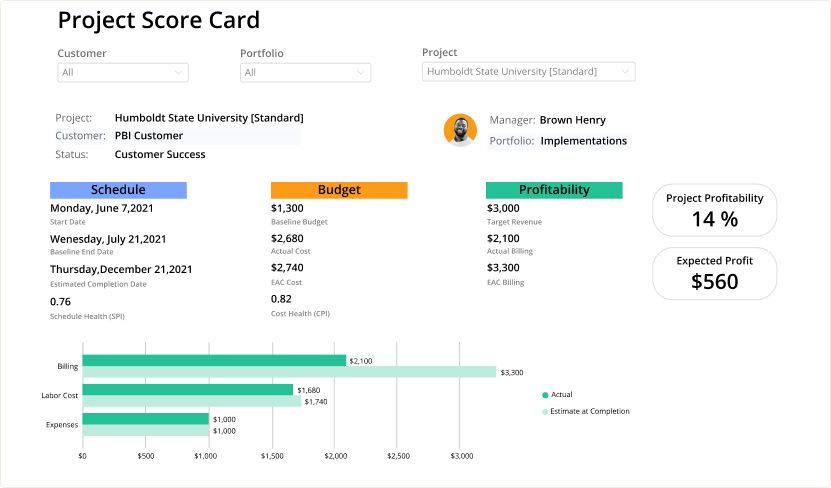
Advanced reporting
BI Reports allow you to visualize, analyze, and interpret data, monitor performance, and gain valuable information on projects, teams, departments, and resources.
Mobile access
Teams should be able to manage projects, check progress, and respond to updates from anywhere using mobile devices. Mobile apps improve flexibility and responsiveness, especially for distributed or field-based teams.
System integrations
A modern project management platform must integrate seamlessly with other business-critical systems such as CRM, ERP, HR software, and communication tools. This reduces duplication, enables real-time data syncing, and enhances operational visibility across departments.
AI-powered forecasting and automation
Advanced tools now include AI capabilities that analyze historical data to predict project risks, estimate completion dates, or suggest task prioritization. AI can also automate routine actions like time tracking, notifications, or resource reallocation, improving speed and accuracy.
Project Management Plan Templates
Project managers can use a project plan template to speed up the creation of a project plan.
Creating a new project based on specific requirements can be challenging. Here are templates for various professional services industries that can serve as a blueprint for each project. They are customizable and available for download as Excel files or via Birdview.
How to choose the right project management software
Choosing the best project management software for your team or company can be complex. The ideal solution depends on your workflows, team size, industry, and level of project complexity.
Here are key factors to consider:
- Ease of use: Is the tool intuitive for new users?
- Customization: Can it adapt to your unique processes?
- Scalability: Will it grow with your business?
- Integration: Does it work with your existing systems like CRM, finance tools, or calendars?
- Support: Is customer service responsive and helpful?
- Security: Are your data and operations protected?
Compare several tools, try demos, involve stakeholders, and always evaluate real use cases before committing.
Project management best practices
There are effective and ineffective ways to manage projects, and while every organization approaches this differently, some foundational principles consistently lead to better results. These best practices are not rigid rules, but flexible guidelines that can be adapted to suit different teams, industries, and company cultures.
Best practices in project management begin with setting clear, measurable goals and building realistic plans that include buffers for risks and delays. Strong communication throughout the project, proactive risk management, and empowering the team to work autonomously are also key to success. Staying focused on client outcomes, maintaining flexibility when priorities shift, and conducting a thorough review at the end of each project help teams continuously improve and deliver better results.
Start managing smarter with the right tools
Project management is not just about completing tasks. It is about aligning teams, resources, and objectives to create real business value. When you understand the key phases, methodologies, and tools involved, you can guide every project from kickoff to completion with greater clarity and control.
With a solution like Birdview PSA, you gain complete visibility into your project portfolio, improve execution, and give your teams the tools they need to deliver on time and within budget.