Whether you’re a seasoned project manager or just starting out, getting a handle on the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) can make a huge difference in how smoothly your projects run. Think of a WBS as your project’s blueprint–it breaks everything down into manageable chunks, making it easier to plan, organize, and control every aspect of your work.
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about WBS. You’ll learn what a WBS is, why it’s crucial for your projects, and how to create and use one effectively. We’ll also cover the different types of WBS, and explore how modern tools like Birdview project management software can make your life a whole lot easier.
What is a work breakdown structure (WBS)?
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a project management tool that breaks down a project into smaller, more manageable components. This hierarchical decomposition allows project managers to define the project’s scope clearly and ensure that all necessary tasks are identified and assigned. The WBS is divided into levels, starting with the overall project at the top and breaking it down into deliverables, tasks, and sub-tasks.
Components of WBS
Understanding a WBS’s key components is crucial for effectively utilizing it. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring its comprehensiveness and practicality.
- Top level: project title
At the very top of the WBS is the project title or the final deliverable. This represents the overall objective or goal of the project. For our example, the top level would be “Develop New Software Application.”
- Second level: major deliverables or phases
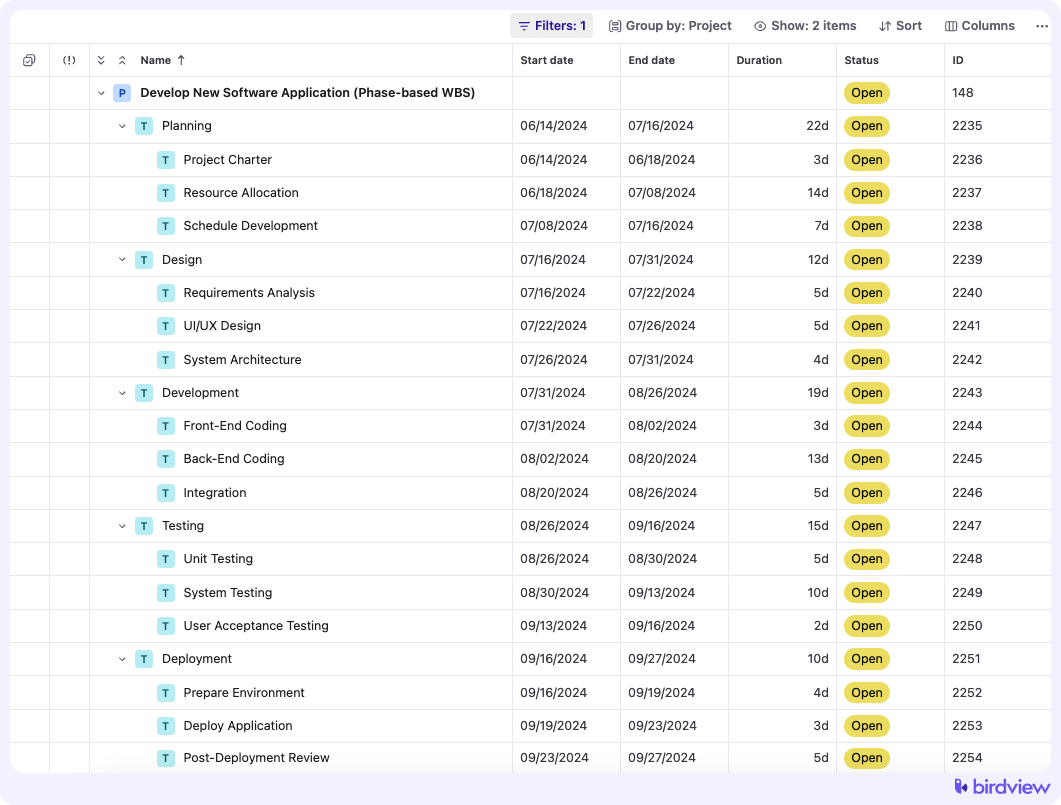
Under the top level, the WBS breaks down into major deliverables or phases of the project. These are significant sections of the project that contribute directly to the overall goal. In the case of “Develop New Software Application,” the second level might include “Planning,” “Design,” “Development,” “Testing,” and “Deployment.”
- Third level: work packages
Each major deliverable is further divided into smaller, more detailed components called work packages. Work packages are specific tasks or groups of tasks that are necessary to complete the deliverable. For example, under “Design,” you might have tasks like “Requirements Analysis,” “UI/UX Design,” and “System Architecture.”
- Fourth level and beyond: sub-tasks
Depending on the complexity of the project, work packages can be further divided into sub-tasks. These are even more detailed activities that ensure every aspect of the task is covered. For instance, “UI/UX Design” could be divided into “Wireframe Creation,” “Prototype Development,” and “User Feedback Sessions.”
- WBS dictionary
Many project managers have created a dictionary to accompany the WBS. This document provides detailed descriptions of each element in the WBS, including definitions, responsible parties, duration, costs, and any other relevant information. The WBS dictionary ensures that everyone involved in the project has a clear understanding of what each component entails.
Types of WBS
A work breakdown structure (WBS) can be organized in different ways depending on your project‘s nature and your team’s preferences. Each type of WBS provides a unique way to break down the project into manageable components.
Choosing the right type of WBS depends on various factors, including the nature of your project, the project management methodology you‘re using, and the specific needs of your stakeholders. Each type of WBS has its strengths and offers a different perspective on the project, helping to ensure all aspects are covered and managed effectively.
Let’s explore the main types of WBS and their examples so you can decide which one suits your project best.
Deliverable-based WBS
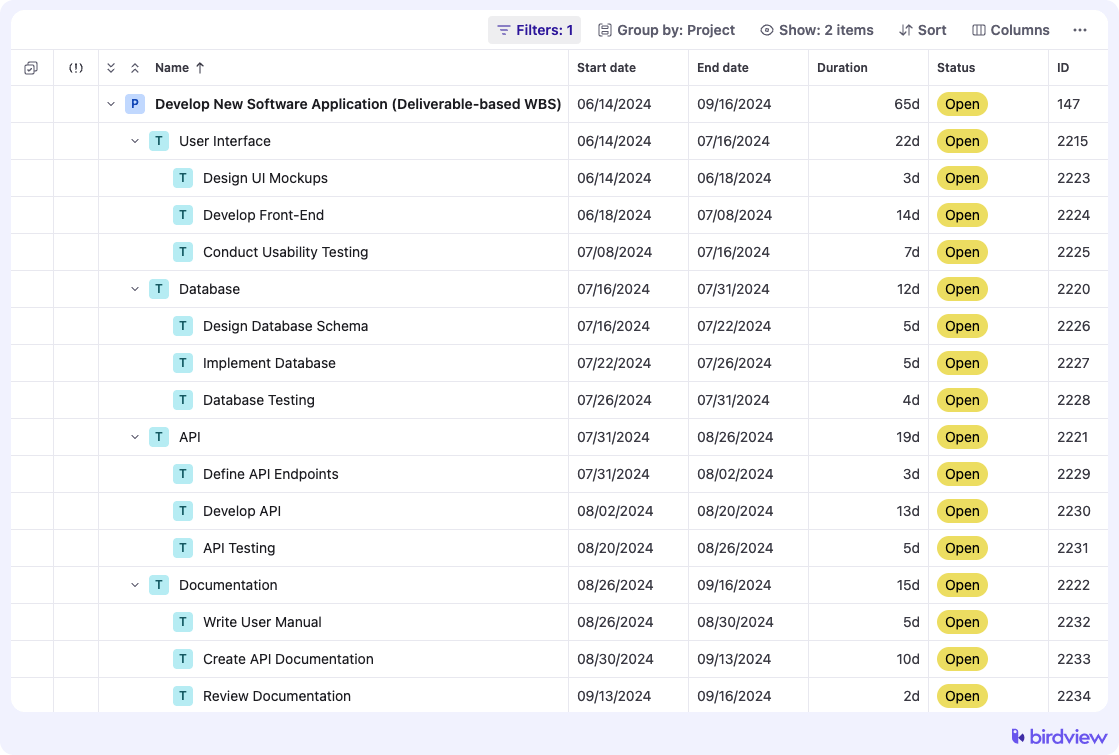
A deliverable-based WBS focuses on the project’s end products or deliverables. This type of WBS breaks down the project into major deliverables and then further into the smaller tasks required to produce these deliverables.
Example: Imagine you‘re managing a software development project. Here‘s what a deliverable-based WBS might look like:
Phase-based WBS
A phase-based WBS breaks down the project according to its phases or stages. This approach is great for projects that follow a sequential process, like the traditional waterfall project management model.
Example: For a software development project, your phase-based WBS might look like this:
Functional WBS
A functional WBS organizes tasks by functional areas or departments. This type of WBS is particularly useful for projects that require significant input from multiple departments or functional areas.
Example: Here‘s what a functional WBS might look like for a software development project:
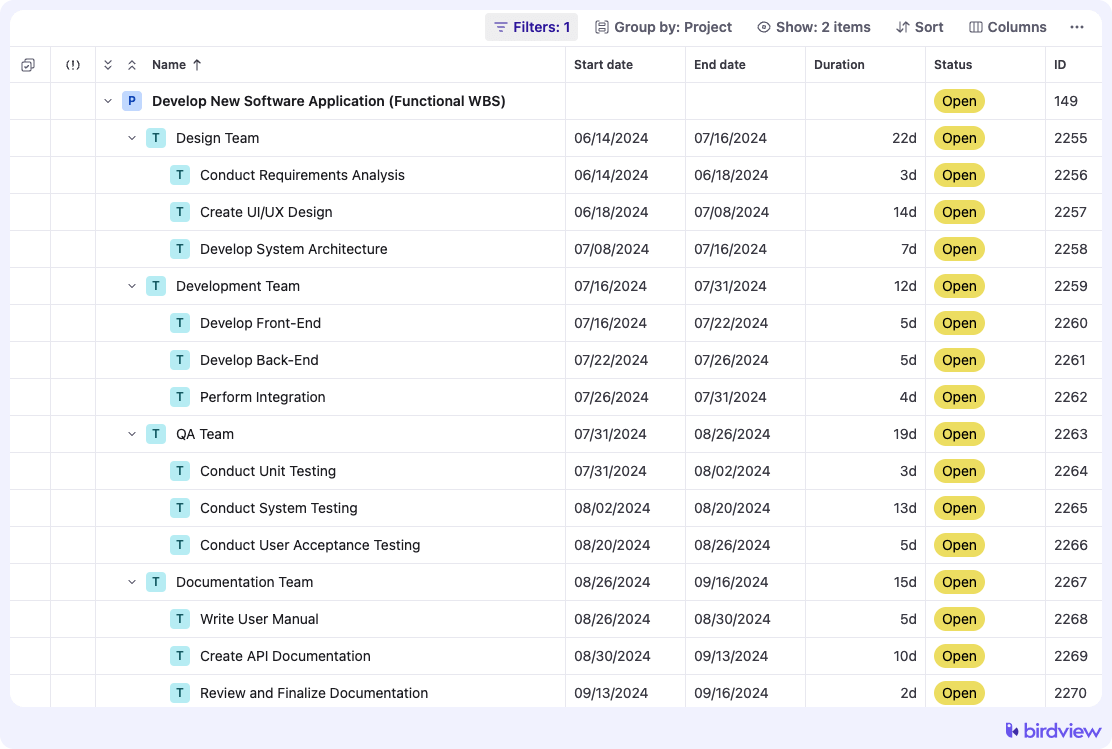
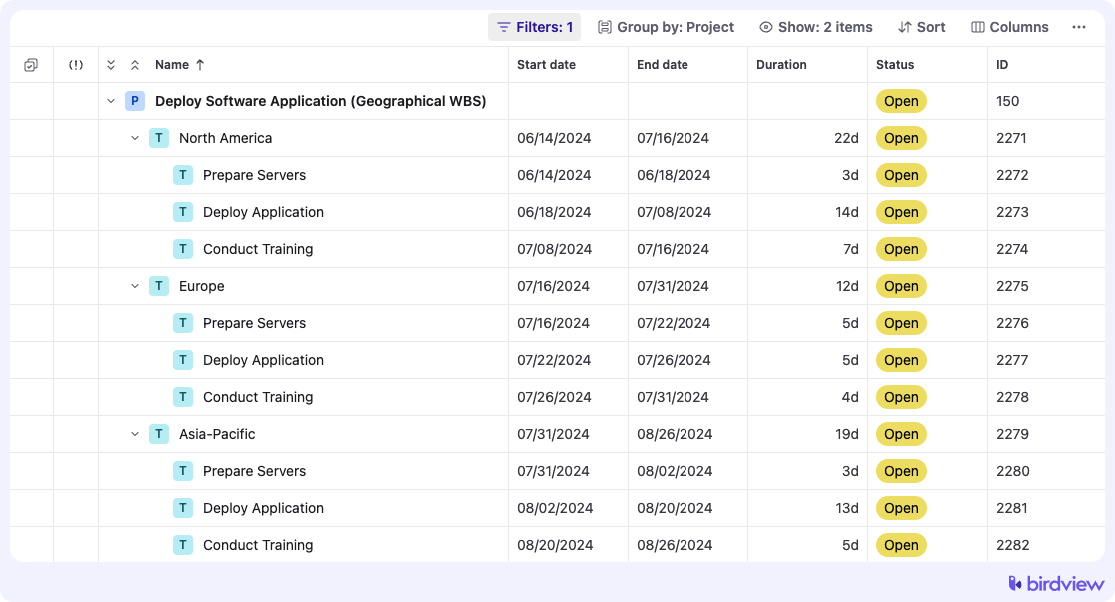
Geographical WBS
A geographical WBS structures the project based on geographic locations. This type of WBS is useful for large-scale projects that span multiple regions, such as international software deployments or multi-site infrastructure projects.
Example: For a software deployment project across multiple regions, a geographical WBS might look like this:
Importance of WBS in project management
A WBS is not just a tool for breaking down tasks; it‘s a framework that ensures your project is organized, manageable, and on track. Let‘s take a look at the key reasons why a WBS is indispensable in project management.
Organizing and defining the scope
- Comprehensive overview: By breaking down the project into smaller components, the WBS provides a comprehensive overview of all the work that needs to be done. This makes it easier to ensure that no essential task is overlooked.
- Scope definition: A well-defined WBS delineates the project’s boundaries. It clearly states what is included in the project scope and, just as importantly, what is not. This helps prevent scope creep, where unplanned tasks and features are added, potentially derailing the project.
- Stakeholder alignment: With a detailed WBS, you can ensure that all stakeholders have a common understanding of the project scope and deliverables. This alignment is crucial for avoiding misunderstandings and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Improving project planning and scheduling
- Detailed scheduling: With a WBS, you can create detailed schedules that outline every task and sub-task. This level of detail makes it easier to set realistic timelines and deadlines for each phase of the project. A well-built WBS will also help you improve overall operational efficiency.
- Resource allocation: The WBS helps in identifying the resources needed for each task. This allows for efficient allocation of resources, ensuring that the right people and materials are available when needed.
- Milestone identification: Breaking down the project into smaller tasks allows for the identification of key milestones. These milestones serve as checkpoints that help track progress and ensure the project stays on course.
Risk management and control
- Early risk identification: By breaking down the project into detailed tasks, potential risks can be identified early in the project lifecycle. This early identification allows for the development of mitigation strategies before risks become issues.
- Control mechanism: The hierarchical nature of a WBS provides a clear framework for monitoring and controlling the project. It allows project managers to track progress at various levels, making it easier to identify deviations and take corrective actions promptly.
- Clear accountability: Each task in the WBS is assigned to a responsible individual or team. This clear assignment of responsibilities ensures accountability and makes it easier to track who is responsible for managing and mitigating specific risks.
Enhancing communication and collaboration
- Common language: A WBS provides a common language and framework for discussing the project. This shared understanding improves communication among team members and stakeholders.
- Collaboration tool: By clearly defining tasks and responsibilities, the WBS fosters team collaboration. Team members can see how their work fits into the larger project and understand the dependencies between tasks.
- Progress reporting: A WBS’s structured nature makes it easier to generate progress reports. These reports can be used to keep stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
Improving cost estimation and budgeting
- Detailed cost breakdown: The WBS allows for a detailed breakdown of costs associated with each task. This granularity ensures that all costs are accounted for and helps in creating a more accurate budget.
- Budget tracking: The WBS makes it easier to track expenses against the budget by associating costs with specific tasks. This tracking helps identify cost overruns early and take corrective actions.
Example: To better illustrate the importance and application of a WBS, let’s consider a practical example. We’ll walk through the development of a new software application, breaking down each phase and task.
- Scope definition: Clearly defining the scope of “Develop new software” ensures all necessary features are included, and unnecessary features are excluded.
- Scheduling: Breaking down the project into phases like Planning, Design, Development, Testing, and Deployment allows for detailed scheduling and realistic deadline setting.
- Risk management: Identifying potential risks at each phase, such as design flaws or integration issues, and developing mitigation strategies.
- Communication: Ensuring that all team members and stakeholders understand the tasks and their interdependencies enhances collaboration and communication.
- Budgeting: Associating costs with tasks such as “UI/UX Design” and “System Testing” ensures a detailed and accurate budget.
How to create a work breakdown structure
Creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) might seem daunting at first, but with a clear approach, you can break it down into manageable steps. A well-crafted WBS will serve as your roadmap for project success, helping you stay organized, allocate resources effectively, and keep everyone on the same page.
1. Define the project goal and objectives
Start by clearly understanding and defining the overall goal and objectives of your project. What are you trying to achieve? This is the foundation upon which your WBS will be built. For example, if your project is to “Develop New Software,” your goal might be to create a user-friendly, efficient, and scalable software application. Involve key stakeholders in this initial step to ensure alignment and clarity, and make sure to document the project goals and objectives clearly.
2. Identify major deliverables and components
Next, break down the project goal into major deliverables or components. These are the big pieces that, when completed, will achieve the project‘s objectives. For developing a new software application, major deliverables might include “User Interface,” “Database,” “API,” and “Documentation.” Think about what needs to be delivered to meet the project goals and group related tasks and outputs together under each deliverable.
3. Breakdown deliverables into manageable tasks
Now, decompose each major deliverable into smaller, more manageable tasks and sub-tasks. This step is crucial for detailed planning and execution. For instance, under “User Interface,” you might have tasks like “Design UI Mockups,” “Develop Front-End,” and “Conduct Usability Testing.” Similarly, for “Database,” tasks might include “Design Database Schema,” “Implement Database,” and “Database Testing.” Ensure tasks are specific and clearly defined, and use action verbs to describe them.
4. Review and refine the WBS
Once you have your initial WBS draft, review it for completeness and accuracy. Involve your team and stakeholders in this review process to ensure nothing is overlooked. Check for missing tasks or components, make sure each task is clear and unambiguous, and confirm that the WBS aligns with the project goals and objectives. This collaborative review helps to fine-tune your WBS and ensure everyone is on the same page.
5. Create a WBS dictionary
Finally, consider creating a WBS dictionary that provides detailed information about each element in the WBS. This includes definitions, responsible parties, durations, costs, and any other relevant details. A WBS dictionary helps ensure that everyone involved in the project understands what each task entails, who is responsible for it, and what resources are required. Clearly describe each task and deliverable, assign responsibilities to team members, and include timelines and resource requirements.
What is WBS software?
Using WBS software can make your life a whole lot easier. These are project management software with WBS functionality that helps you create and manage your work breakdown structure more efficiently, allowing you to stay organized and keep your project on track. With WBS software, you can visualize your project‘s scope, enhance collaboration, and ensure better resource allocation, all while maintaining control over your timelines and budgets. You can try creating your own work breakdown structure in the free Birdview trial.
Must-have features of WBS software
There are many project management tools available on the market, but they all differ. When choosing one, focus on the presence of the most important features. Taking Birdview as an example, let‘s have a look at the features that ensure the tool meets all your project management needs and helps you work more effectively.
- User-friendly interface
A user-friendly interface is essential for getting everyone on your team up to speed quickly. Look for software with an intuitive layout, drag-and-drop functionality, and easy access to all necessary tools. This way, your team can focus on the project instead of struggling with the software.
- Customizable templates
Customizable templates save you time and effort, especially if you handle similar projects regularly. With the ability to create and save templates, you can quickly set up new projects using predefined structures. This ensures consistency and efficiency across all your projects. Check out Birdview‘s free work breakdown structure templates.
- Integration with other tools
Your WBS software should integrate well with other project management and collaboration tools you use, like Microsoft Project, Jira, or Slack. This seamless integration allows data to flow smoothly between different platforms, reducing manual updates and minimizing errors.
- Collaboration features
Effective project management requires collaboration, and your WBS software should make this easy. Look for features like real-time updates, task comments, file sharing, and notifications. These features ensure that your team can communicate easily, stay updated on progress, and share information without needing to switch between different platforms.
- Real-time updates and progress tracking
Real-time updates and progress tracking are crucial for monitoring your project‘s status at any given moment. This feature helps you identify bottlenecks early, make necessary adjustments, and keep everyone informed about the project‘s progress. It also ensures that everyone is working with the most current information, reducing the chances of miscommunication.
- Reporting and visualization tools
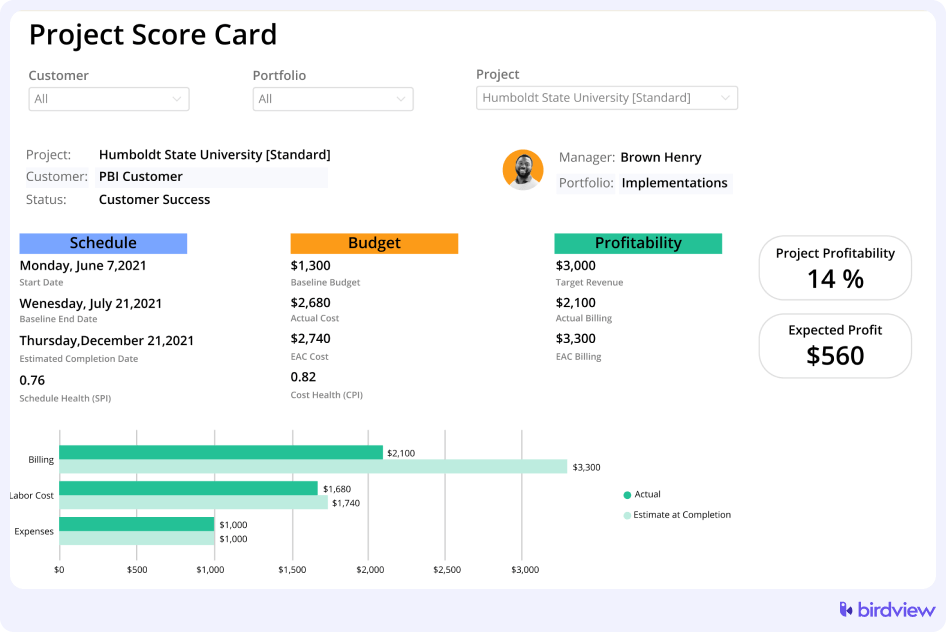
Comprehensive reporting and visualization tools help you analyze project data and make informed decisions. Look for software that offers customizable reports, Gantt charts, and dashboards. These tools provide a visual representation of your project‘s status, helping you quickly understand progress, identify issues, and communicate effectively with stakeholders.
- Scalability
If you manage projects of varying sizes and complexities, scalability is key. Your WBS software should handle both small and large projects without compromising performance. This way, as your project grows, your software can support the increasing demands without requiring you to switch tools.
Work breakdown structure examples
Now that you have a solid understanding of what a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is and how it can benefit your projects, let‘s look at some real-life examples. These examples will show you how a WBS can be applied in different scenarios, from civil engineering projects to software development and marketing campaign planning.
Civil engineering
Successfully implementing a WBS to manage a complex civil engineering project and its deliverables can greatly enhance project clarity and efficiency. Here’s a work breakdown structure example for a road construction project:
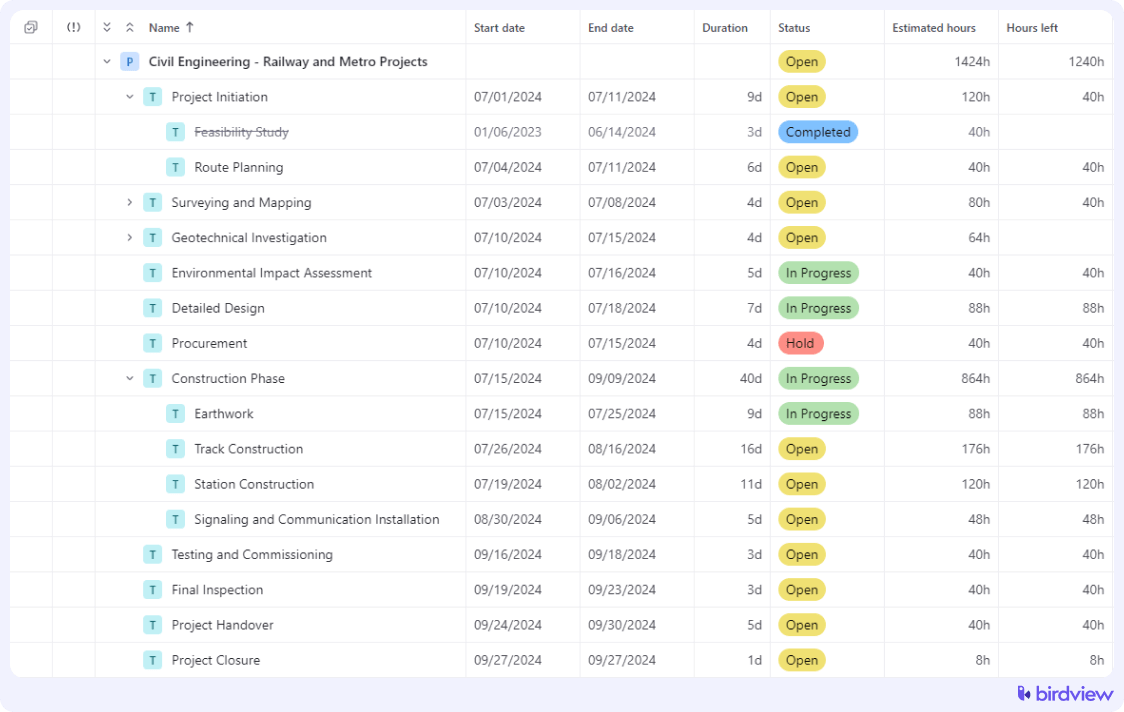
Free work breakdown structure templates for civil engineering.
Software development
Using a WBS to break down development phases and manage functional teams helps ensure every aspect of the software development lifecycle is covered – while gaining full visibility on SDLC provides critical transparency into process bottlenecks, team collaboration, and pipeline health.. Here‘s a work breakdown structure example for a software development project:
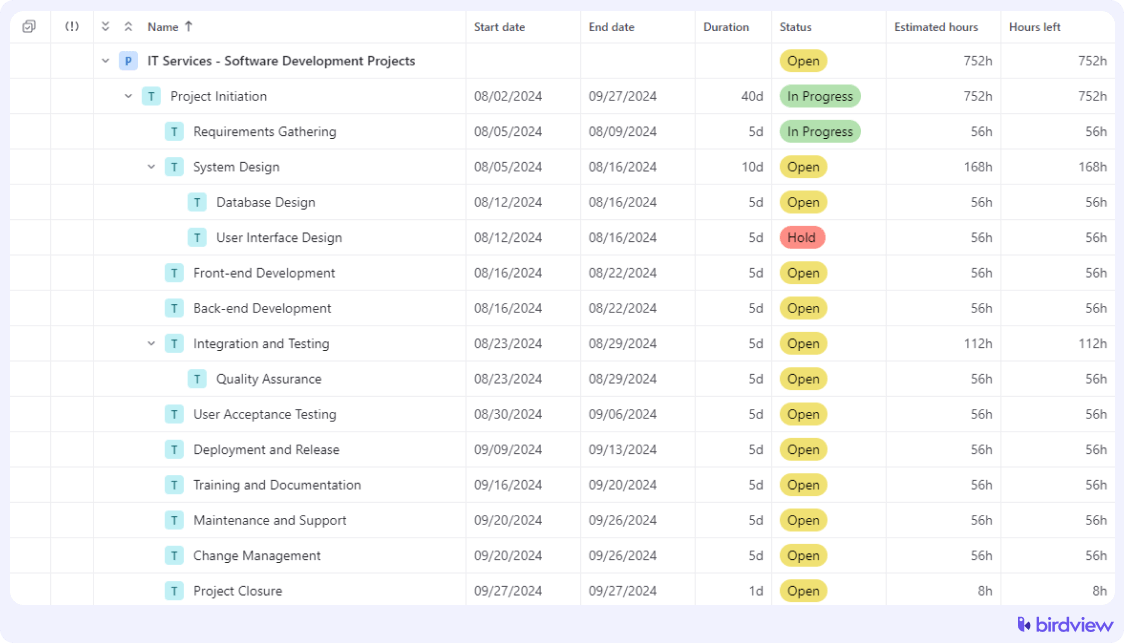
Free work breakdown structure templates for IT services.
Business consulting
Structuring tasks and deliverables for a business consulting project using a WBS ensures all its elements are organized and managed effectively. Here‘s a work breakdown structure example for a financial consulting service:
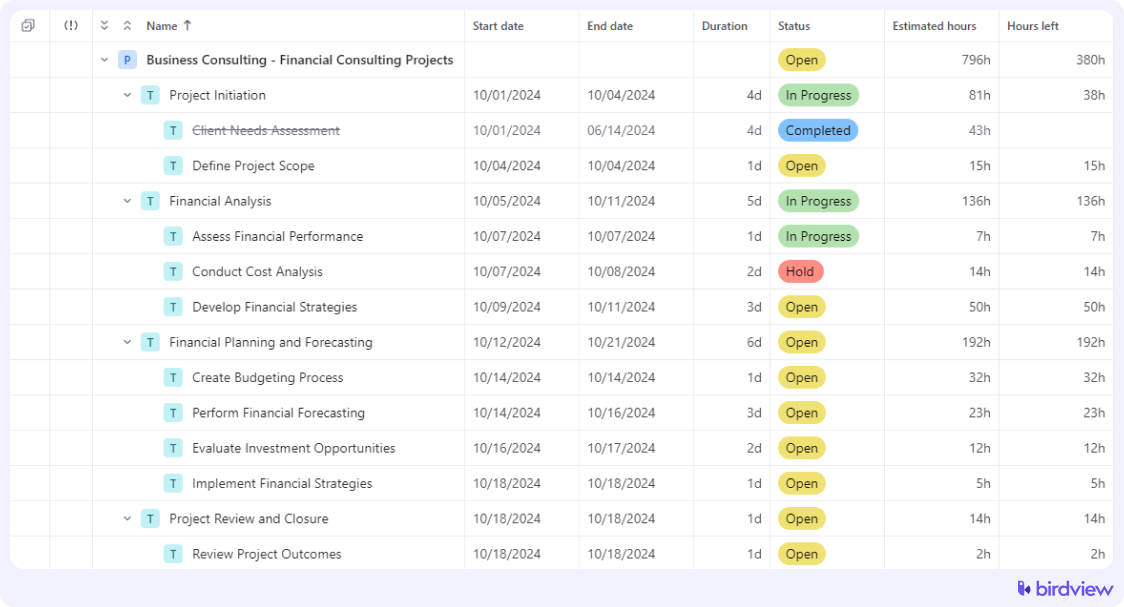
Free work breakdown structure templates for business consulting.
Final thoughts
A well-crafted WBS breaks down complex projects into manageable tasks, providing a clear roadmap from start to finish. A WBS ensures that all aspects of the project are covered.
Incorporating a WBS into your project management practices can significantly enhance your ability to deliver projects on time, within scope, and on budget. Tools like Birdview further simplify the process, offering features that support planning, collaboration, and progress tracking.
Sign up for a free 14-day trial that can be extended up to 28 days to explore Birdview possibilities, or schedule a demo call with one of our managers to walk you through the platform.