Capacity utilization measures how much of a company’s potential output is actually being used. Knowing this rate helps businesses understand how well they use their resources and meet demand. Without it, you risk wasting resources and missing opportunities for increased output. Using tools like Birdview PSA can really help here. It automatically calculates capacity for you. No more manual tracking! It saves time and gives you real-time insights that you can‘t get from old methods.
What is capacity utilization?
Capacity utilization measures how much of a company’s potential production capacity is being used. It compares the actual output with the maximum possible output if all resources were fully engaged.
For professional services firms, capacity utilization metric tracks how well employees’ time is spent on client projects. A low utilization rate might suggest that talent is underused, while a high rate could mean staff are stretched too thin.
In physical product-producing companies, capacity utilization highlights how well equipment, labor, and materials are used to meet production targets. If the rate is low, it may signal missed opportunities or an underestimation of demand, while a higher rate could point to strong production but risks of overloading.
Explore ▶️ Resource underutilization: Causes and solutions explained
Capacity utilization formula
To calculate capacity utilization, follow this simple formula 👇:
| Capacity Utilization = (Actual Output / Potential Output ) x 100 |
Where:
- Actual Output: The quantity of goods or services produced during a specific period.
- Potential Output: The maximum quantity of goods or services that could be produced with all available resources.
Explore ▶️ What is utilization rate? How to track & calculate
How to calculate capacity utilization? Step-by-step guide
Here‘s how you can calculate your capacity utilization in four simple steps.
Step 1: Determine actual output
Find the total quantity of goods or services produced during a specific time period. This is your actual output.
Here‘s how you can calculate it 👇:
| Actual Output = Total Quantity of Goods or Services Produced |
For example, if a consulting firm completed 150 projects in a quarter, their actual output would be 150.
Step 2: Find potential output
Identify the maximum quantity of goods or services your organization can produce if it operates at full capacity.
Here‘s how you can calculate it 👇:
| Potential Output = Maximum Quantity of Goods or Services Possible |
For instance, if that same consulting firm could complete 300 projects per quarter at full capacity, then the potential output is 300.
Step 3: Calculate capacity utilization
Once you have both actual output and potential output, divide the actual output by the potential output, then multiply by 100 to express it as a percentage, to find the capacity utilization rate.
Here‘s how you can calculate it 👇:
| Capacity Utilization Rate = (Actual Output / Potential Output) × 100 |
For example:
Capacity Utilization Rate = (150 / 300) x 100 = 50%
This means you’re using 50% of your potential production capacity.
Step 4: Analyze the result
The result shows the percentage of your total capacity that is being used. If your capacity utilization rate (CUR) is below 100%, you’re not using all available resources.
If it‘s above 100%, you‘re overloading your capacity, which could lead to strain.
Example analysis:
The consulting firm’s rate of 50% shows it‘s operating below its full capacity. This could signal underutilization of resources or inefficiencies.
It may need to adjust its operations, improve resource allocation, or increase demand to close the gap.
Interpreting the capacity utilization results
👉 Low utilization rate: If the rate is much lower than 85%, it could indicate you’re not fully using your resources and could be missing out on potential production. It may also point to weak demand.
👉 High utilization rate: If the rate is above 100%, it suggests that you are operating beyond your capacity, which may stress your resources.
👉 Ideal range: Generally, a capacity utilization rate (CUR) between 85% and 100% is considered ideal.
Industry benchmarks for capacity utilization rates
Standard industry rates
Capacity utilization rates can differ widely by industry. Here‘s a quick look at typical ranges:
- Manufacturing: Ideal rates are between 80% and 90%. This allows businesses to produce proactively without overburdening their resources.
- Services: These industries often have lower utilization rates due to fluctuating demand patterns.
- Technology: In software and tech development, utilization rates tend to be lower, often between 60% and 75%.
How to use benchmarks to evaluate your performance?
By comparing your CUR to industry benchmarks, you can see how well you‘re using your resources. If your CUR is much lower than the benchmark, it may signal underutilization.
On the other hand, a higher CUR could indicate inefficiencies or the risk of overworking your resources.
The role of automation and technology in increasing capacity utilization rates
Automation and data-driven decisions are key to improving capacity utilization rates. Here’s how they can help:
▶️ Automation: Using tools like AI-powered systems (e.g., Birdview PSA) can streamline operations, cut down on errors, and increase productivity. Automation helps reduce bottlenecks, lower costs, and make better use of resources.
▶️ Data-Driven Decisions: With the help of data analytics, companies can make smarter decisions about how to adjust their capacity based on real-time data. By understanding trends, predicting demand, and forecasting capacity, businesses can avoid overproduction or underutilization.
The best tool for capacity utilization tracking: Birdview PSA
Managing team capacity, especially with remote teams and fluctuating workloads, can be challenging. Without clear visibility, it‘s easy to end up with mismatches between what‘s needed and what‘s available. This can result in resources being either underused or overworked, which harms productivity and adds stress.
Additionally, inaccurate forecasting can mess up project timelines and budgets.
And this is where capacity tracking tools come in.
Capacity tracking tools monitor and measure the utilization of available resources, such as workforce, equipment, or production facilities. These tools help identify whether resources are fully used, underutilized, or overloaded.
By tracking real-time data, they enable better planning, scheduling, and allocation of tasks. They also provide insights into trends, helping you anticipate future needs and make adjustments to improve productivity.
Businesses can use these tools to balance workloads, reduce bottlenecks, and avoid unnecessary downtime.
How capacity tracking tools like Birdview PSA help?
Birdview PSA simplifies resource capacity tracking by providing real-time insights into how your resources are being used. You‘ll quickly spot any capacity gaps in capacity and be able to make adjustments.
It also helps you match the right person to the right task, based on their skills and availability, keeping the workload fair and manageable.
✅ Birdview PSA‘s approach to capacity utilization tracking
Capacity tracking & resource utilization reports
1. Resource loading report
Resource loading report shows you exactly how much work each team member has on their plate. It helps you spot who‘s overloaded and who has extra capacity. That way, you can quickly balance the workload and make sure no one is overwhelmed.
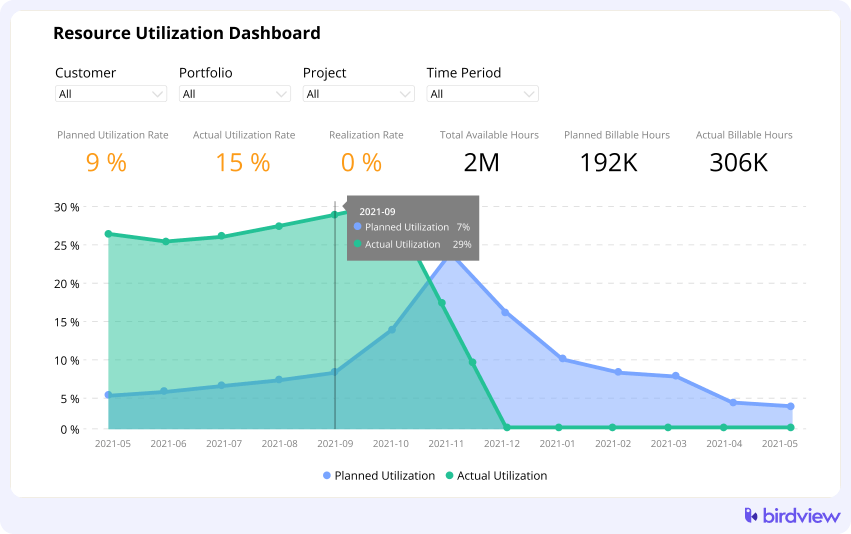
2. Resource utilization dashboard
The resource management dashboard gives you a visual snapshot of how your team is performing. It shows how well resources are being used and points out any gaps. With this information, you can step in and make adjustments to get the team back on track.
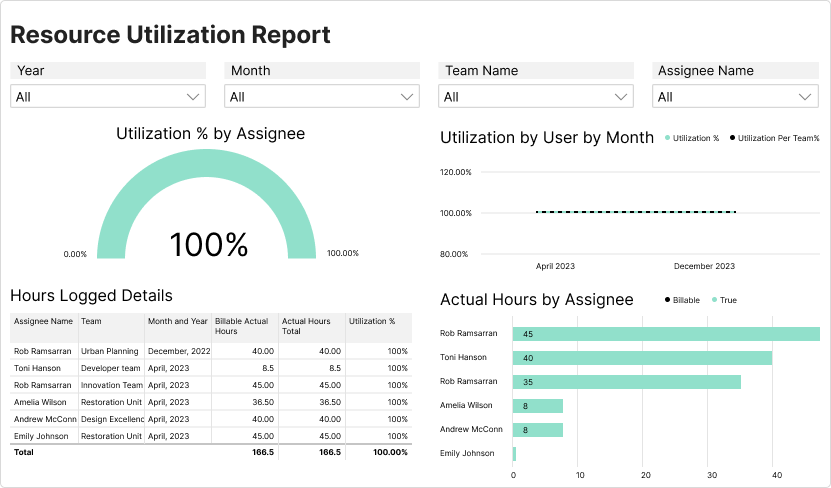
✅ Birdview PSA‘s time tracking and reporting features
Advanced time tracking for accurate capacity tracking
Birdview PSA connects time tracking directly to capacity tracking. It captures both billable and non-billable hours, linking them to resource usage so you can spot patterns and better manage time allocation.
With timesheets and payroll reports, it‘s easy to identify patterns and make informed decisions to improve how resources are used and how revenue is managed.
Automated reporting
Birdview PSA provides advanced reporting tools to help you understand your projects and resources better. The customizable BI reports and dynamic dashboards give a snapshot of your team‘s productivity and project progress.
You can adjust these reports to fit your organization‘s needs, helping you find ways to allocate resources smarter and plan more proactively.
By having all the data at your fingertips, you can make informed choices to keep projects on track and deliver better outcomes.
✅ Integration with other tools for seamless capacity tracking
Birdview PSA‘s integrations
Birdview PSA integrates with popular tools like Microsoft Outlook, Jira, and Salesforce to make capacity tracking easier. It automatically syncs schedules, project updates, and resource data, cutting down on manual effort.
✅ AI and machine learning for predictive capacity management
AI-driven predictions
Birdview PSA uses AI to predict issues that could delay projects or increase costs. By looking at past data and team performance, AI spots potential problems before they happen.
For example, it can predict if a project is at risk of falling behind schedule or going over budget because of resource shortages. This gives teams a chance to fix things early, avoiding delays.
Reduce risks with machine learning
Machine learning takes it further by analyzing past projects, resource use, and team performance to forecast future outcomes. This helps businesses make adjustments ahead of time, preventing bottlenecks and delays.
If something looks off, like a task taking longer than expected, teams can make changes before it affects the whole project.
Better capacity forecasts
Birdview PSA also improves capacity forecasts by using real-time data. With more accurate insights, businesses can plan resource use better.
✅ Client and team collaboration for better resource planning
Collaboration features
Birdview PSA makes it easy to collaborate and work together via its set of collaboration tools. You can invite guest users, like clients and stakeholders, to stay updated on project progress and resource use.
Everyone is kept in the loop with real-time notifications that cover key activities, such as task completions and resource changes.
Team members can easily track their workload and deadlines, so there are no surprises. If resource capacity changes, the system sends out notifications to alert the team. This lets everyone adjust quickly without causing delays.
✅ Benefits of using Birdview PSA as a capacity tracking tool
| Benefit | Description |
| Real-Time Insights into Resource Load | Birdview PSA offers a live view of your team‘s workload, allowing you to see exactly how much work each team member is handling. Managers can quickly adjust workloads to balance tasks and keep projects on schedule. |
| Optimize Resource Allocation | Birdview PSA helps you identify underused or overworked team members and allows you to move resources where needed. |
| Improve Forecasting Accuracy | Using past data and project timelines, Birdview PSA predicts future capacity requirements, helping you plan for hiring or adjustments and make better decisions based on accurate forecasts. |
| Eliminate Burnout Risks | Birdview PSA tracks workloads and resource allocation, making it easy to spot imbalances and prevent team members from getting overworked, helping reduce burnout and keep your team productive. |
| Manage Multiple Projects Simultaneously | Birdview PSA‘s project portfolio management feature lets you allocate resources across different projects, ensuring your team‘s capacity is maximized and maintaining balance across ongoing projects. |
Why does measuring capacity utilization matter?
Tracking capacity utilization helps businesses make the most of their resources, whether it‘s machinery, staff, or time. By understanding how much of your resources are being used, you can make smarter decisions.
Relying on data, rather than guesswork, leads to better productivity and higher profits.
Regularly measuring capacity utilization allows you to identify underused resources and areas that need attention. If you ignore this, you might end up wasting resources, lowering productivity, and losing out on revenue.
Capacity utilization use cases
Capacity utilization helps leaders in different roles make smarter decisions. Let‘s dive into how various leaders can use capacity utilization to improve performance. 👇
1️⃣ Executive leadership (CEO, CFO, COO)
Use case: strategic planning and profitability
Professional services: CEOs use capacity utilization to figure out if teams are being overworked or underused. This directly impacts revenue and client satisfaction. CFOs look at it to predict how much revenue they‘ll make, based on how many hours the team can bill and what resources are available.
Product companies: COOs look at how well manufacturing plants are performing. They want to make sure production matches demand and that equipment isn‘t being underused or overburdened. CFOs check if the company‘s income covers the fixed costs and investments needed for machinery or staff.
Key questions they ask:
- Are we making the most of our resources to drive profitability?
- Should we invest in expanding our capacity (people, machines, or infrastructure)?
- How can we improve utilization to increase margins?
2️⃣ Operations managers
Use case: resource allocation and process efficiency
Professional services: Operations managers track how much time staff, such as consultants, lawyers, or developers, are working. They aim to balance workloads, avoiding burnout, while keeping clients happy. They also look for idle time that could be used for other tasks.
Product companies: Managers focus on making sure equipment is used properly, so machines aren‘t sitting idle or running too hard. They adjust production schedules to meet demand and avoid overproduction or shortages, and they also manage labor to avoid downtime.
Key questions they ask:
- Are we using resources the best way possible?
- Where are the slowdowns in our processes?
- How can we reduce idle time and improve productivity?
3️⃣ Project managers
Use case: project planning and staffing
Professional services: Project managers use capacity utilization to schedule team members based on their availability. They avoid overbooking and keep track of billable vs. non-billable hours to make sure projects are profitable.
Product companies: Project managers look at production timelines, balancing machine and worker availability. They also plan maintenance schedules so that downtime doesn‘t affect project deadlines, and they manage production to meet seasonal demand.
Key questions they ask:
- Do we have enough resources to meet deadlines?
- Are any team members overbooked or underused?
- How can we adjust schedules to stay on track?
4️⃣ HR and workforce planners
Use case: talent management and workforce optimization
Professional services: HR teams use capacity utilization to predict hiring needs. They identify when workloads are too heavy for the current team and where additional help is needed. They also track the balance between billable and non-billable tasks to prevent employee burnout.
Product companies: Workforce planners look at trends in production capacity to plan when to hire or train more staff. They also manage staffing levels to avoid too many or too few workers, especially during peak seasons.
Key questions they ask:
- Do we need more staff, or can we make better use of the current team?
- Are employees overworked or underutilized?
- How can we balance billable and non-billable tasks better?
5️⃣ Sales and account managers
Use case: capacity forecasting and sales pipeline management
Professional Services: Sales teams track capacity utilization to know how much additional work their team can take on. They align their sales pipeline with available resources to avoid overpromising to clients. When handling larger deals, they figure out if extra resources are needed.
Product companies: Sales managers make sure production levels match sales forecasts to avoid running out of stock or having excess inventory. They work closely with operations to plan production runs and adjust sales targets based on available capacity.
Key questions they ask:
- Do we have the resources to take on new clients or projects?
- Should we prioritize certain deals based on capacity limitations?
- How can we improve alignment between sales and operations?
6️⃣ Financial analysts
Use case: cost management and profitability analysis
Professional services: Financial analysts track revenue per employee and use capacity utilization to spot any underused resources. This helps them predict profitability and find areas where costs could be cut.
Product companies: Analysts look at how capacity affects production costs. They calculate the break-even point for production and assess how idle time impacts fixed costs. They also search for ways to improve profitability by improving production processes.
Key questions they ask:
- How does capacity utilization impact profits?
- Are we operating at the right capacity for profitability?
- How can we lower costs from underutilization?
7️⃣ IT and systems administrators
Use case: capacity planning for it resources
Professional services: IT teams manage servers and software to make sure systems can handle workloads without performance issues or downtime.
Product companies: IT administrators make sure that infrastructure, like ERP or MES systems, has the capacity to support production schedules. They focus on avoiding downtime that could cost the company money.
Key questions they ask:
- Are our IT systems operating at their full potential?
- Do we need to scale up infrastructure to meet future needs?
- How can we reduce downtime and improve system performance?
Industry-specific capacity utilization examples 👇
| Industry | Role | Use Case |
| Engineering | Project Manager | Track how engineers are allocated to different projects to meet deadlines. |
| IT Consulting | Operations Manager | Monitor billable hours to make sure consultants are fully used. |
| Architecture | Workforce Planner | Assign architects and designers to projects based on their availability. |
| Business Consulting | Partner/Manager | Balance client projects to keep teams busy but avoid overworking them. |
| Advertising Agencies | Account Manager | Track how creative teams are used to meet deadlines without burnout. |
| Marketing | Campaign Manager | Make sure the team is fully used during campaigns, avoiding any idle time. |
| Oil and Gas | Field Supervisor | Monitor the use of drilling equipment and staff to reduce idle time. |
| Healthcare | Hospital Administrator | Track the use of medical staff and equipment to make sure quality patient care. |
| Manufacturing | Production Manager | Measure how often machines are used to optimize production and maximize output. |
Types of capacity utilization
Let‘s break down different types of capacity utilization by category. 👇
1️⃣ Workforce capacity utilization
Workforce capacity utilization looks at how your employees are contributing to your business goals. Here‘s what to focus on: 👇
Subtypes:
- Billable utilization: Measures how much time employees spend on revenue-generating tasks compared to non-billable activities.
- Non-billable utilization: Tracks time spent on internal activities like meetings or training.
- Productive utilization: Looks at the time spent on tasks that directly drive business outcomes.
- Idle capacity utilization: Identifies time when employees are available but not assigned to projects.
- Overtime utilization: Tracks additional time worked beyond regular hours.
- Specialist utilization: Measures how often highly skilled or specialized employees are called upon for specific tasks.
Applicable to:
- IT Consulting
- Business Consulting
- Advertising Agencies
2️⃣ Machine capacity utilization
This category is necessary in industries like manufacturing, where machinery plays a central role. Here are some important types: 👇
Subtypes:
- Available capacity utilization: Shows how much of the available machine time is put to productive use.
- Effective capacity utilization: Compares actual production with what machines could potentially produce under optimal conditions.
- Idle time utilization: Measures periods when machines remain inactive.
- Downtime utilization: Focuses on the time lost due to maintenance, malfunctions, or failures.
- Peak Capacity utilization: Examines machine use during high-demand periods, making sure production aligns with market needs.
Applicable to:
- Engineering
- Manufacturing
3️⃣ Space capacity utilization
This tracks how physical spaces are used, including offices, warehouses, and retail areas. Key types are: 👇
Subtypes:
- Office space utilization: Looks at how office spaces are allocated among employees and teams.
- Warehouse utilization: Tracks how storage spaces are used for inventory management.
- Retail space utilization: Measures the effectiveness of store layouts and customer traffic.
- Production floor utilization: Observes how well manufacturing floors are utilized during production cycles.
Applicable to:
- Architecture
- Engineering
- Retail
4️⃣ Project capacity utilization
For businesses handling multiple projects, this category tracks resource allocation. Key types include: 👇
Subtypes:
Resource utilization by project: Tracks resource allocation for each project, making sure balance across initiatives.
Project utilization rate: Measures the proportion of available project resources used in relation to planned capacity.
Overlapping project utilization: Focuses on how resources are divided across multiple projects happening simultaneously.
Capacity buffer utilization: Tracks how much extra time is used to account for unexpected delays or issues.
Applicable to:
- Business Consulting
- IT Consulting
- Advertising Agencies
5️⃣ Financial capacity utilization
This category measures how financial resources are spent in relation to the company’s operational needs. Key areas include: 👇
Subtypes:
- Cost capacity utilization: Looks at whether costs are in proportion to the capacity used during production.
- Revenue capacity utilization: Measures revenue generated against the organization‘s overall capacity.
- Fixed cost utilization: Assesses how fixed costs such as rent and salaries are covered by available resources.
Applicable to:
- Business Consulting
- IT Consulting
6️⃣ Energy capacity utilization
This category tracks how energy resources are consumed. Important aspects include: 👇
Subtypes:
- Electricity utilization: Monitors electricity consumption against the potential available capacity.
- Fuel utilization: Tracks how fuel resources are being used during operations.
- Renewable energy utilization: Measures the portion of energy that comes from renewable sources, providing insight into sustainability.
Applicable to:
- Engineering
- Manufacturing
7️⃣ IT Infrastructure capacity utilization
This category tracks the use of a company‘s digital infrastructure. Key areas include: 👇
Subtypes:
- Server capacity utilization: Measures how much of the server‘s total capacity is being used.
- Network capacity utilization: Focuses on bandwidth consumption across the network.
- Cloud utilization: Tracks how much of the cloud resources are being used compared to what‘s allocated.
- Software license utilization: Looks at how software licenses are distributed and used across teams.
Applicable to:
- IT Consulting
- Business Consulting
8️⃣ Time capacity utilization
This category tracks how time is distributed across tasks. Important areas include: 👇
Subtypes:
- Shift utilization: Tracks how well work shifts are managed and utilized.
- Task Utilization: Focuses on how time is spent on specific tasks and projects.
- Overtime utilization: Measures how often overtime is used to meet deadlines.
- Idle time utilization: Tracks periods of inactivity among employees or machines.
Applicable to:
- All Industries
9️⃣ Production line capacity utilization
For manufacturing businesses, this measures how well production lines are used. Key types include: 👇
Subtypes:
- Full line utilization: Measures the proportion of time the production line is fully operational.
- Bottleneck utilization: Focuses on the slowest process in the production line and its effect on overall throughput.
- Changeover time utilization: Tracks the time spent switching between different production runs, impacting the overall line performance.
Applicable to:
- Engineering
- Manufacturing
🔟 Customer capacity utilization
This category focuses on how resources directly interacting with customers are used. Important areas include: 👇
Subtypes:
- Support team utilization: Tracks how much time customer support teams spend on solving customer issues.
- Client project utilization: Measures resource allocation for ongoing client projects, making sure clients‘ needs are met.
- Appointment utilization: Focuses on the usage of appointment slots for customer-facing services, like consultations or support calls.
Applicable to:
- Advertising Agencies
- Business Consulting
- IT Consulting
The strategy behind capacity utilization
Capacity utilization is all about making the most of your resources–whether it‘s your team, equipment, or processes. It’s a balancing act between what your business can handle and what the market demands.
Get the balance right, and you‘ll cut waste, save money, and stay ahead of the competition.
1. Internal factors influencing capacity utilization
These are the things inside your business that affect how well you use your resources:
a) Workforce efficiency
A skilled and well-organized team works faster and reduces delays, helping to produce more.
b) Equipment maintenance
Taking care of equipment keeps it running smoothly, avoiding breakdowns and keeping production on track.
c) Process optimization
Simplifying and improving workflows removes unnecessary steps, making production faster and more focused.
2. External factors that impact capacity utilization
These are outside influences that businesses must adapt to:
a) Market demand fluctuations
When demand changes, businesses need to adjust production–ramping up when demand is high and cutting back when it‘s low to avoid waste.
b) Seasonal trends
Certain products have peak seasons. Adjusting capacity to match these trends, like producing winter clothes in winter, keeps resources from being underused.
c) External shocks
Unexpected events, such as supply chain issues or economic changes, can disrupt operations. Businesses must adjust quickly to maintain production.
How to balance capacity utilization?
Balancing capacity utilization is about making the best use of resources without overloading or leaving them idle. Striking this balance helps maintain productivity and supports consistent operations.
Here‘s a closer look at the risks of imbalance and how to achieve a healthy balance.
1. Risks of overutilization
Pushing resources too hard can lead to significant problems. Here‘s what can happen when systems or staff are overused: 👇
Burnout: Overworked employees and machines can break down, leading to interruptions, higher error rates, and costly repairs.
Quality problems: Rushing work often results in lower-quality output, which can hurt customer satisfaction or require rework.
Process bottlenecks: When certain tasks or processes are overloaded, delays build up and slow down overall operations.
💡 Takeaway! Overutilization stretches resources too far, leading to mistakes, delays, and lower performance.
2. Risks of underutilization
Underusing resources may seem harmless, but it can have negative consequences for productivity and profitability. Here‘s why: 👇
Wasted costs: Idle staff or equipment still incur costs even when they‘re not producing anything. This reduces overall profitability.
Missed opportunities: Unused capacity could have been directed toward new projects or meeting higher demand.
Poor resource management: When resources aren‘t allocated properly, it becomes harder to achieve goals or scale operations.
💡 Takeaway! Underutilization limits growth and can result in unnecessary expenses.
3. Optimal capacity utilization
Achieving optimal capacity utilization involves thoughtful planning and regular adjustments. Here‘s how you can do it: 👇
Distribute workload evenly: Avoid overloading one team or piece of equipment while others remain idle. Review operations regularly to keep workloads steady.
Adapt in real time: Use data and feedback to monitor how resources are being used and make adjustments as needed. For instance, you can shift tasks or adjust schedules to handle fluctuations in demand.
Support consistent outcomes: When resources are used thoughtfully, production remains steady, costs stay manageable, and the quality of work is consistent.
💡 Takeaway! Balancing capacity allows your business to stay on track and maintain steady progress without unnecessary strain.
How to increase capacity utilization?
If you’re looking to get the most out of your production resources, increasing capacity utilization is key. Here are some simple and beneficial ways to improve it.
1. Optimizing production schedules
Adjust your production schedules to match real-time demand. This helps reduce idle time and makes sure that production aligns with when it’s needed most.
By syncing work shifts with demand peaks, you can get the most out of your available resources and avoid wasted time.
2. Cross-training employees
Investing in cross-training your staff is a smart move. If employees are trained to operate different machines or handle multiple tasks, they can step in wherever needed.
This flexibility prevents delays, keeps things running smoothly, and helps maintain steady productivity across different areas.
3. Upgrading equipment and technology
Modernizing your equipment can make a huge difference. Replacing old machines with new, more efficient ones increases your production capacity without the need for extra labor.
Upgrading your technology and tools helps you produce more with the same resources.
4. Reducing downtime
Unexpected breakdowns can seriously affect capacity. To prevent this, implement a solid preventive maintenance plan.
Schedule routine checks and repairs to keep machines in good shape, so they‘re less likely to stop unexpectedly. This helps reduce downtime and keep everything running at full capacity.
5. Balancing labor and equipment
Make sure your staffing levels match your machine capacity. When labor is in sync with the machines, it prevents both underutilization and overstaffing.
This balance makes sure your resources are being used as proactively as possible.
Practical ways to improve utilization without major capital investments
Here are a few simple ways to get more out of your current resources:
▶️ Process optimization
Small changes in your processes can make a big impact. For example, reorganizing workstations or streamlining workflows can help improve product flow. A better layout can reduce unnecessary movement, save time, and prevent bottlenecks in production.
▶️ Adjusting operational practices
Minor adjustments to how you manage your operations can lead to smoother processes. Reorganizing inventory or changing task assignments can help. You could also experiment with shift patterns or optimize machine setups. These small tweaks can help increase output without the need for extra costs or resources.
What are the effects of low and high-capacity utilization?
| Low Capacity Utilization
👉Wastes resources 👉Increases per-unit costs 👉Reduces profitability |
High Capacity Utilization
👉Strains resources 👉Increases employee stress 👉May lower product quality |
How to reduce downtime and bottlenecks?
Here‘s how to tackle downtime and bottlenecks 👇
1️⃣ Identifying and analyzing bottlenecks
To reduce bottlenecks, begin by observing how your processes flow. Look for areas where activity slows down or stops. Bottlenecks can occur for numerous reasons, such as:
- Outdated or malfunctioning tools or systems
- Ineffective process steps or workflows
- Delays in resource availability
Signs of bottlenecks include inconsistent output or long wait times between steps. By monitoring these issues closely, you can pinpoint the root cause.
2️⃣ Addressing specific bottleneck areas
Once you‘ve identified the bottlenecks, focus on improving the problem areas. Common solutions involve:
- Upgrading tools or systems: Replacing outdated resources can speed up operations.
- Reallocating tasks: If team members are overloaded, consider redistributing work to avoid delays.
- Strengthening resource relationships: Delays in obtaining required resources can cause hold-ups, so it‘s important to have reliable sources.
Addressing these areas will help eliminate the bottleneck and improve the flow of activities.
3️⃣ Implementing improvement techniques
Improvement techniques can help you reduce waste, minimize downtime, and raise productivity. Two useful approaches are:
- 5S: This method focuses on organizing the work environment for better performance. It stands for Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.
- Continuous Improvement: This approach encourages regular improvements by making small, ongoing adjustments. Continuous improvement helps detect problems early and prevent new bottlenecks from forming.
By implementing these techniques, you not only fix existing bottlenecks but also create a system that prevents new ones from happening.
What is the difference between capacity planning and capacity utilization?
| Aspect | Capacity Planning | Capacity Utilization |
| Definition | Capacity planning is about predicting what resources will be needed in the future. | Capacity utilization shows how much of your current production capacity is being used. |
| Focus | Focuses on matching resources with future demand. | Focus on how well your current resources are being used. |
| Objective | Aims to use resources wisely, avoiding too many or too few. | Aims to compare how much you are producing now versus how much you could produce. |
| Time Frame | Long-term, based on future needs. | Short-term, based on what is happening now. |
| Outcome | Tells you how many resources are needed for future production. | Shows the percentage of capacity you’re using right now. |
| Use in Decision-Making | Helps with planning for future needs and investments. | Helps assess how well current resources are being used and where improvements are needed. |
Capacity utilization vs. operational efficiency: Difference
| Aspect | Capacity Utilization | Operational Efficiency |
| Definition | Measures the percentage of potential output that is actually produced. | Focuses on how well a company uses its resources to produce goods. |
| Focus | Focused on the output in relation to total potential. | Focused on reducing waste, time, and cost during the production process. |
| Key Metric | Capacity Utilization Rate = (Actual Output ÷ Potential Output) × 100 | Efficiency Ratio = (Actual Output ÷ Input Resources Used) |
| Indicators | A low utilization rate means resources are underused. | Low performance means resources or time are wasted. |
| Impact | Affects the cost per unit: higher utilization lowers costs. | Directly impacts productivity and the overall cost structure. |
| Goal | Maximize the use of production capacity. | Maximize resource use while cutting down on waste. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the economic significance of capacity utilization?
Capacity utilization shows how well resources are being used. A high rate suggests strong demand and growth, while a low rate may point to a slowdown. It can also affect prices–low utilization might lead to falling prices, while high utilization can push prices up.
What is capacity utilization in business?
In business, capacity utilization compares actual production to a company‘s full potential. It helps identify how much of the company‘s resources are being used and if there‘s room for improvement.
Does investment go up when the capacity utilization rate is high?
Yes, when capacity utilization is high, companies often increase investment. This is because high demand signals the need for more production, encouraging businesses to expand or add resources.
What is capacity utilization in the manufacturing industry?
In manufacturing, capacity utilization measures how much of the available production capacity is used. A high rate shows that resources are being put to good use, while a low rate suggests underuse and missed opportunities.
How does capacity utilization affect the business cycle?
Capacity utilization plays a big role in the business cycle. When it‘s high, the economy tends to grow, with more jobs and spending. When it‘s low, it often signals a downturn, affecting overall growth.
What is 80% capacity utilization?
An 80% capacity utilization rate means a company is using 80% of its full production potential. This is usually a good level, showing that resources are being used well without being overstrained.
What are corporate capacity utilization rates?
Corporate capacity utilization rates (CUR) reflects how seamlessly a company uses its resources. A higher CUR often leads to reduced unit costs, as production scales up. But it’s important not to overextend. Pushing resources too far can increase operational risks, impacting long-term sustainability.
What are historical capacity utilization rates?
Looking at your company‘s CUR over time can give you valuable insights into your performance. By tracking this data, you can spot trends like underutilization (when resources are being wasted) or overutilization (when you’re pushing past your limits).
Economists also use historical CUR data to gauge the health of the economy. For example:
- Low CUR could indicate a downturn or lack of demand.
- High CUR often points to growth, as more resources are being used to meet higher demand.
What is the difference between capacity utilization and productivity?
Capacity utilization measures how much of a company‘s production potential is used, while productivity focuses on how much output is generated per unit of input.
How capacity utilization affects customer satisfaction and delivery times?
High capacity utilization can help businesses meet customer demand quickly, improving satisfaction. But if the company is stretched too thin, it may lead to delays and affect delivery times.
Conclusion
Tracking and optimizing capacity utilization plays a huge role in uplifting productivity and making the most of your resources. With the right tools, you can quickly spot inefficiencies and prevent roadblocks from slowing you down.
▶️ Birdview PSA is a great solution for this, offering real-time insights and features that simplify resource management. By proactively allocating resources, you‘ll avoid gaps, balance workloads, and keep your team focused on what matters.
With Birdview PSA, managing capacity becomes a breeze, helping you keep projects on track and moving forward smoothly, without the usual hiccups.



